Unveiling the Secrets of the Atmosphere: A Deep Dive into Isobaric Weather Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of the Atmosphere: A Deep Dive into Isobaric Weather Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of the Atmosphere: A Deep Dive into Isobaric Weather Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Secrets of the Atmosphere: A Deep Dive into Isobaric Weather Maps
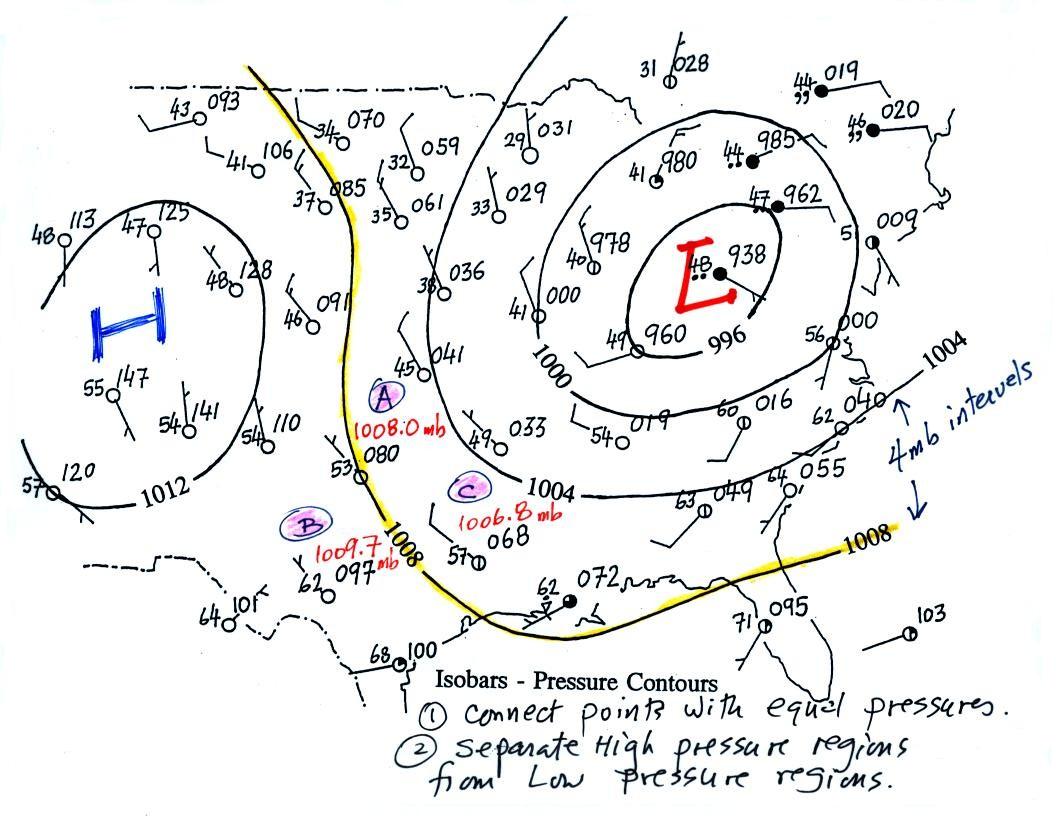
The Earth’s atmosphere is a dynamic entity, constantly in motion, driven by the interplay of temperature, pressure, and wind. Understanding these complex interactions is crucial for predicting weather patterns and ensuring safety for various human activities, from aviation to agriculture. One tool that provides invaluable insight into atmospheric dynamics is the isobaric weather map.
The Essence of Isobars
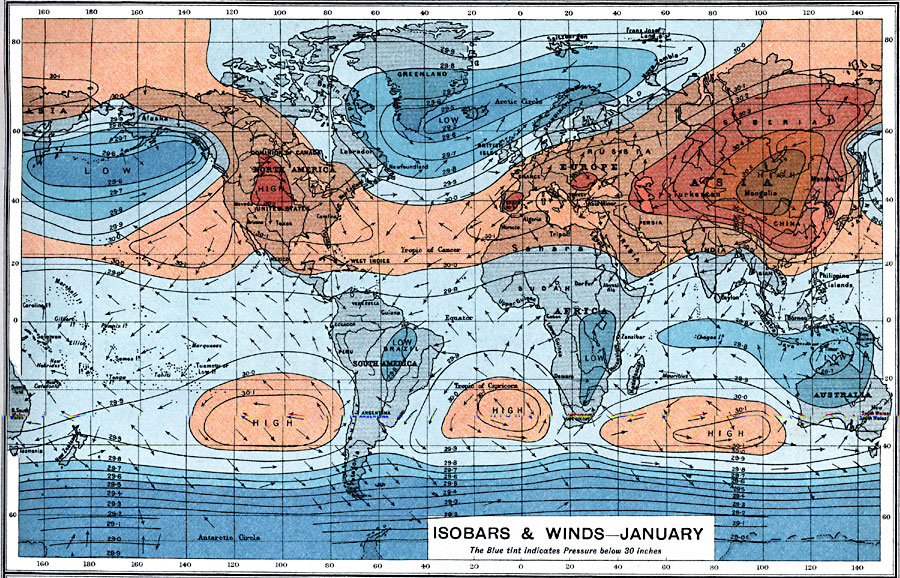
Isobaric weather maps, often referred to simply as isobars, are graphical representations of atmospheric pressure at a specific altitude. The term "isobar" itself signifies "equal pressure," and these maps depict lines connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure. The closer the isobars, the steeper the pressure gradient, indicating a stronger wind. Conversely, widely spaced isobars suggest a gentle pressure gradient and weaker winds.
A Visual Guide to Atmospheric Pressure
Isobars are typically drawn on weather maps using a standardized system. Lines are typically drawn at intervals of 4 millibars (mb), with thicker lines representing higher pressure values. The pressure values are usually indicated at specific points along the lines, allowing for precise interpretation.
Deciphering the Language of Isobars
Isobaric maps are not merely static representations of pressure. They offer a dynamic window into the forces driving atmospheric circulation. Here’s how to interpret their key features:
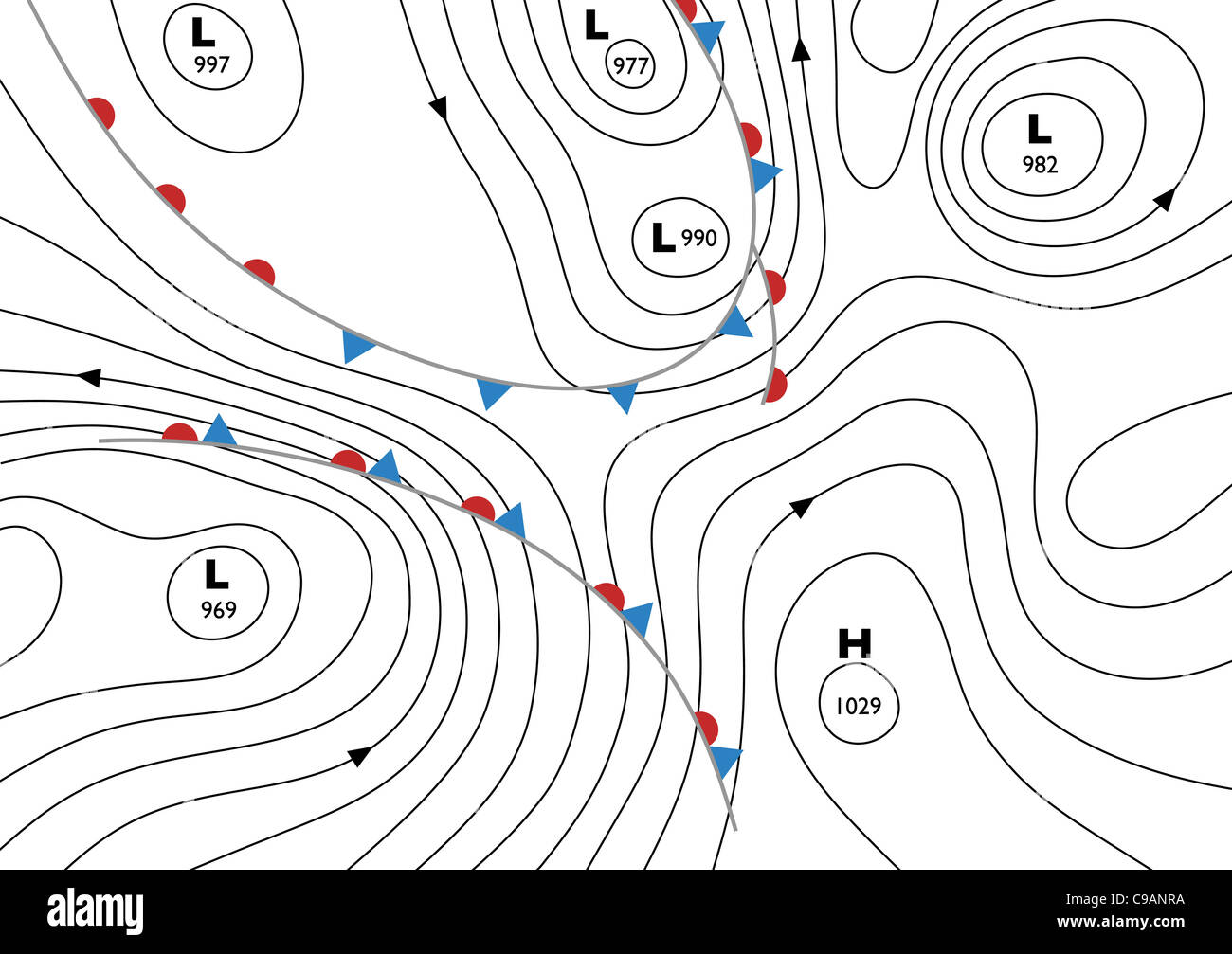
- High-Pressure Systems (Anticyclones): These systems are characterized by closed isobars forming a circular pattern with higher pressure at the center. High-pressure systems are associated with calm, clear skies, and generally stable weather conditions. Air descends in high-pressure systems, leading to the formation of clear skies and the absence of clouds.
- Low-Pressure Systems (Cyclones): Low-pressure systems are depicted by closed isobars encircling a center of low pressure. These systems are associated with unsettled, often stormy weather. Air rises in low-pressure systems, leading to cloud formation and precipitation.
- Pressure Gradient: The distance between isobars reflects the pressure gradient. A steep pressure gradient, indicated by closely spaced isobars, signifies strong winds. Conversely, a gentle pressure gradient, represented by widely spaced isobars, indicates weaker winds.
- Wind Direction: Isobars provide valuable insights into wind direction. In the Northern Hemisphere, winds flow counterclockwise around low-pressure systems and clockwise around high-pressure systems. In the Southern Hemisphere, the directions are reversed.
- Jet Streams: These narrow bands of strong winds, located high in the atmosphere, are depicted on isobaric maps as areas of rapid pressure changes. Jet streams play a significant role in steering weather systems and influencing temperature patterns.
Beyond the Basics: Unveiling the Depth of Isobaric Maps
While the core principles of isobaric maps are relatively straightforward, their application extends far beyond basic weather interpretation. They are instrumental in:
- Forecasting Weather: By analyzing the movement and interaction of pressure systems, meteorologists can predict weather patterns with a high degree of accuracy. This information is crucial for public safety, particularly in regions prone to severe weather events.
- Aviation Safety: Isobaric maps are essential for aviation safety. Pilots use these maps to understand wind patterns and potential turbulence, enabling them to plan routes and optimize flight conditions.
- Marine Navigation: Mariners rely on isobaric maps to navigate safely. They use these maps to predict wind and wave patterns, helping them avoid hazardous conditions and optimize their voyages.
- Agricultural Planning: Farmers use isobaric maps to understand prevailing wind patterns, which can influence crop yields and irrigation strategies. This information is particularly valuable for managing crops susceptible to wind damage or requiring specific wind conditions for pollination.
- Environmental Monitoring: Isobaric maps provide valuable insights into atmospheric circulation patterns, which are crucial for monitoring air quality, tracking pollution dispersion, and understanding climate change impacts.
FAQs: Demystifying Isobaric Weather Maps
1. What is the difference between a surface pressure map and an isobaric map?
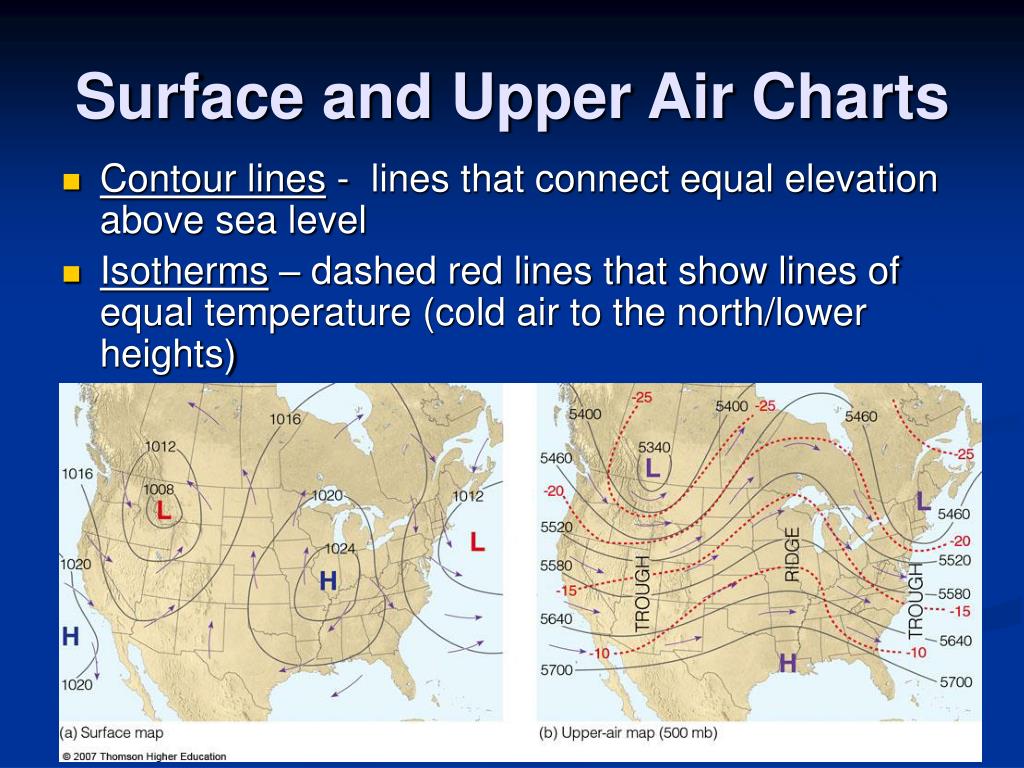
A surface pressure map depicts atmospheric pressure at ground level, while an isobaric map represents pressure at a specific altitude. Isobaric maps are more informative for understanding atmospheric circulation patterns and predicting weather events.
2. How are isobaric maps used to predict weather?
By analyzing the movement and interaction of high and low-pressure systems, meteorologists can predict weather patterns. The steepness of the pressure gradient, indicated by the spacing of isobars, provides insight into wind strength and direction, which are key factors in weather forecasting.
3. Can isobaric maps be used to predict the intensity of storms?
Yes, isobaric maps can be used to predict the intensity of storms. The closer the isobars, the stronger the pressure gradient, indicating a stronger wind and potentially a more intense storm.
4. How do isobaric maps help in aviation safety?
Isobaric maps provide pilots with valuable information about wind patterns and potential turbulence, enabling them to plan routes and optimize flight conditions, enhancing aviation safety.
5. Are isobaric maps used for climate change research?
Yes, isobaric maps are used in climate change research. By analyzing long-term trends in atmospheric pressure patterns, scientists can gain insights into how climate change is impacting global circulation patterns and weather events.
Tips for Effective Isobaric Map Interpretation
- Understand the Scales: Pay close attention to the pressure scales used on the map, as these can vary depending on the source.
- Focus on the Pressure Gradient: The spacing of isobars reveals the pressure gradient, indicating wind strength and direction.
- Consider the Altitude: Isobaric maps represent pressure at a specific altitude, which is typically indicated on the map.
- Recognize High and Low-Pressure Systems: Identify closed isobars representing high and low-pressure systems, as these are key indicators of weather conditions.
- Combine with Other Weather Data: Isobaric maps are most informative when combined with other weather data, such as temperature, humidity, and wind speed.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Understanding the Atmosphere
Isobaric weather maps are invaluable tools for understanding and predicting atmospheric dynamics. By providing a visual representation of pressure patterns, they reveal the intricate interplay of forces driving weather events and influencing various human activities. From forecasting storms to guiding aviation and maritime navigation, isobaric maps continue to play a crucial role in ensuring safety, optimizing operations, and advancing our understanding of the Earth’s dynamic atmosphere.
/isobarmap-56a9e0d25f9b58b7d0ffa3cf.gif)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of the Atmosphere: A Deep Dive into Isobaric Weather Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!