Unraveling the Tapestry of Chilean Patagonia: A Geographical Exploration
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of Chilean Patagonia: A Geographical Exploration
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of Chilean Patagonia: A Geographical Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Tapestry of Chilean Patagonia: A Geographical Exploration

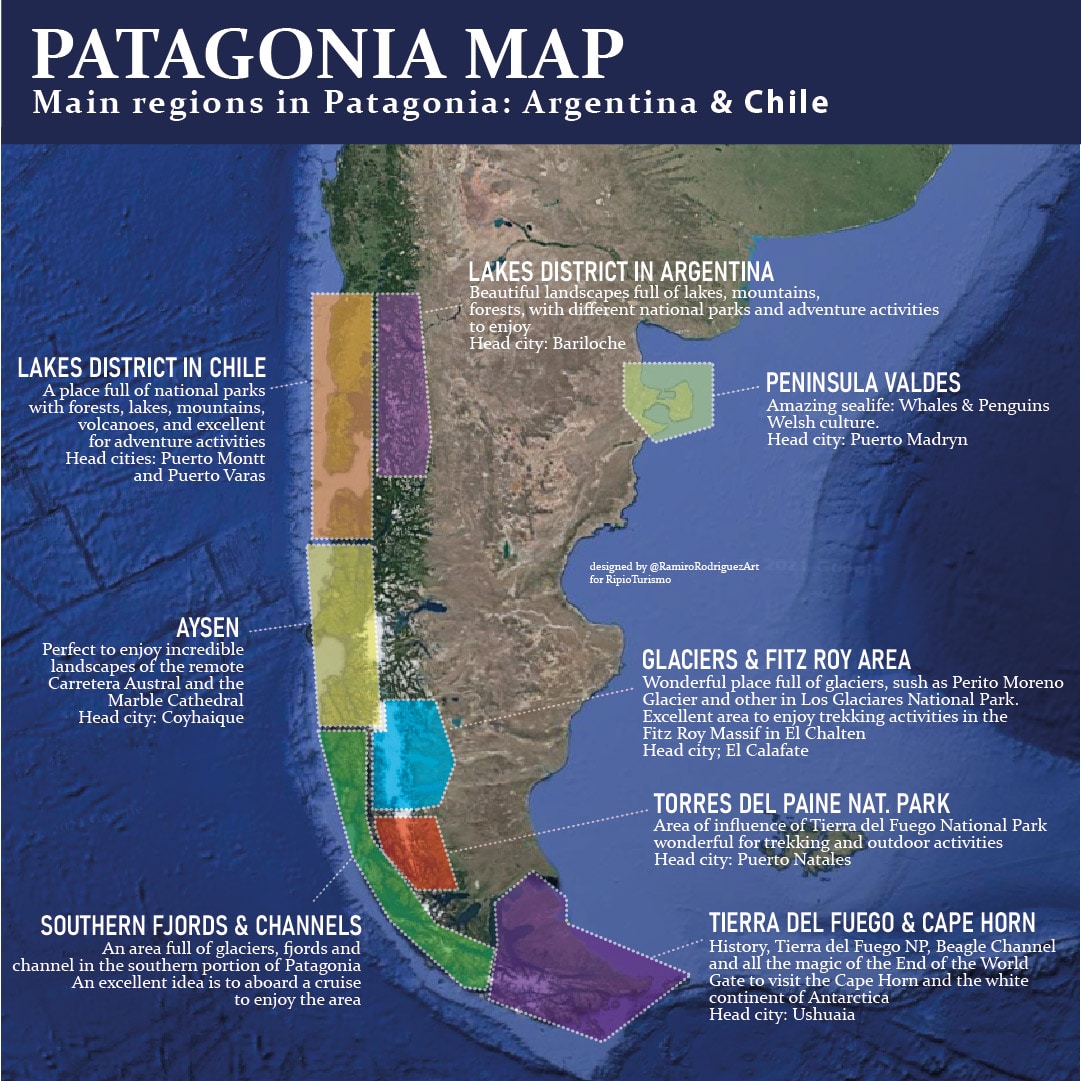
Patagonia, a land of stark beauty and untamed wilderness, stretches across the southernmost reaches of South America, encompassing both Chile and Argentina. While Argentina claims a larger portion of this vast region, Chilean Patagonia holds a unique allure, characterized by its dramatic landscapes, diverse ecosystems, and rich cultural heritage. Understanding the geography of Chilean Patagonia through its map is crucial to appreciating the region’s captivating beauty and its significance within the global context.
A Land Shaped by Nature’s Force:
Chilean Patagonia’s map is a testament to the powerful forces that shaped this land. The Andes Mountains, a formidable spine running the length of South America, rise dramatically in the east, casting long shadows over the region. Their towering peaks, sculpted by glaciers and volcanic eruptions, are a defining feature of the landscape. The Andes are not merely a physical barrier but also a climatic divider, creating distinct microclimates on either side.
To the west, the Pacific Ocean exerts its influence, carving out a rugged coastline punctuated by fjords, inlets, and islands. The interplay between the ocean and the mountains creates a dynamic landscape, where glaciers descend from the peaks to meet the sea, carving out magnificent fjords like the iconic Fiordland National Park.
A Tapestry of Diverse Ecosystems:
The map of Chilean Patagonia showcases a remarkable diversity of ecosystems, each with its own unique flora and fauna. The northern regions, characterized by a Mediterranean climate, boast forests of Chilean pine and evergreen shrubs, while the central region is dominated by the Patagonian steppe, a vast expanse of grasslands and scrubland.
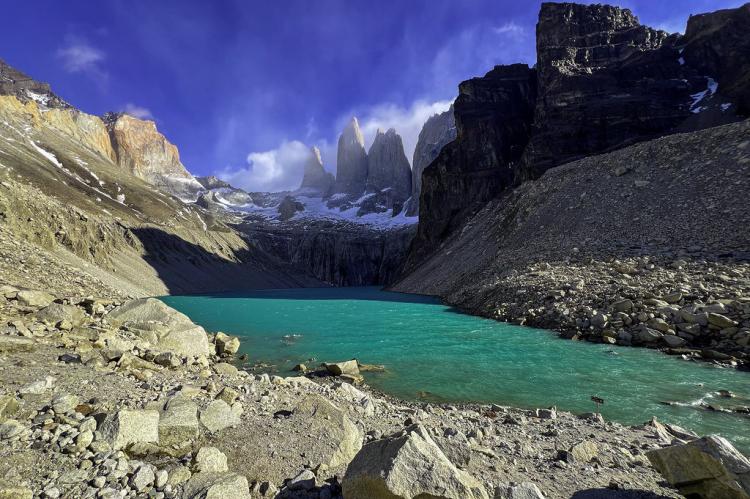
Further south, the landscape transforms into a realm of glaciers, ice fields, and towering mountains. The iconic Torres del Paine National Park, with its granite peaks and turquoise lakes, is a testament to the region’s glacial beauty. The southernmost region, Tierra del Fuego, is a land of windswept plains, dense forests, and dramatic fjords, where the boundaries of the world seem to blur.
Navigating the Map: Key Geographic Features:
1. The Andes Mountains:
The Andes Mountains, a defining feature of Chilean Patagonia, run parallel to the Pacific Coast. Their highest peaks, like Mount San Valentín (4,058 meters) and Mount Cerro Paine (3,050 meters), dominate the landscape, creating a dramatic backdrop for the region’s iconic national parks.
2. The Patagonian Ice Fields:
The southern portion of Chilean Patagonia is home to vast ice fields, including the Southern Patagonian Ice Field, the world’s largest continental ice field outside of Antarctica. These ice fields are a source of numerous glaciers that descend into the valleys and fjords, sculpting the landscape and creating breathtaking glacial lakes.
3. The Chilean Fjords:
The Pacific Coast of Chilean Patagonia is characterized by deep, narrow inlets called fjords. These dramatic waterways, carved by glaciers over millennia, offer stunning views of the surrounding mountains and forests. Notable fjords include the Last Hope Sound, the Eyre Fjord, and the Baker Fjord.
4. The Strait of Magellan:
The Strait of Magellan, a narrow waterway separating mainland South America from Tierra del Fuego, is a historically significant passage connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. It played a crucial role in maritime exploration and trade, and it continues to be an important route for shipping today.
5. The Beagle Channel:
The Beagle Channel, a picturesque waterway separating Tierra del Fuego from Isla Navarino, is a popular destination for wildlife viewing and scenic cruises. It is known for its diverse birdlife, including Magellanic penguins, and its stunning views of the surrounding mountains and glaciers.
Beyond the Map: The Human Story:
The map of Chilean Patagonia tells not only a story of nature but also a story of human resilience and adaptation. Indigenous communities, such as the Mapuche and the Kawésqar, have inhabited this land for centuries, living in harmony with its diverse ecosystems. Their traditional knowledge and practices have shaped the cultural landscape of the region.
The arrival of European settlers in the 19th century brought about significant changes, including the introduction of sheep farming, the development of mining industries, and the establishment of national parks. These developments have had both positive and negative impacts on the region’s environment and its indigenous communities.
FAQs About Chilean Patagonia:
1. What is the best time to visit Chilean Patagonia?
The best time to visit Chilean Patagonia depends on your interests. For hiking and trekking, the summer months (December to February) offer the most pleasant weather. However, for wildlife viewing, the spring and autumn months (September to November and March to May) are ideal.
2. What are the major attractions in Chilean Patagonia?
Chilean Patagonia offers a plethora of attractions, including Torres del Paine National Park, the Perito Moreno Glacier, the Carretera Austral, and the fjords of the southern region.
3. How do I get to Chilean Patagonia?
The primary gateway to Chilean Patagonia is the city of Punta Arenas, which is accessible by air from Santiago and other major cities in Chile. From Punta Arenas, you can travel by road, boat, or plane to other destinations in the region.
4. What are the best places to stay in Chilean Patagonia?
Chilean Patagonia offers a wide range of accommodation options, from luxury lodges to budget-friendly hostels. The best place to stay depends on your budget and your interests.
5. What are the best things to do in Chilean Patagonia?
Chilean Patagonia offers a range of activities, including hiking, trekking, kayaking, horseback riding, wildlife viewing, and glacier trekking.
Tips for Exploring Chilean Patagonia:
1. Pack for all weather conditions:
Chilean Patagonia is known for its unpredictable weather, so pack layers of clothing, including waterproof jackets, rain pants, and warm sweaters.
2. Be prepared for physical exertion:
Many activities in Chilean Patagonia require physical exertion, so be sure to pack comfortable hiking boots and appropriate clothing.
3. Research local customs and traditions:
Chilean Patagonia has a rich cultural heritage, so take the time to learn about the local customs and traditions before your trip.
4. Respect the environment:
Chilean Patagonia is a fragile ecosystem, so be mindful of your impact on the environment and follow Leave No Trace principles.
5. Be patient and flexible:
Chilean Patagonia is a remote and challenging destination, so be prepared for delays and unexpected changes in plans.
Conclusion:
The map of Chilean Patagonia is a powerful tool for understanding the region’s unique geography and its diverse ecosystems. It reveals a land of dramatic beauty, where mountains meet the sea, glaciers carve out fjords, and wildlife thrives in a range of habitats. By understanding the map, we can appreciate the region’s significance as a natural wonder and a cultural treasure, and we can better navigate its challenges and opportunities. Chilean Patagonia, with its rugged beauty and untamed spirit, continues to inspire awe and wonder, reminding us of the power and resilience of nature.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of Chilean Patagonia: A Geographical Exploration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!