The Punic Wars: A Map of Conflict and Consequence
Related Articles: The Punic Wars: A Map of Conflict and Consequence
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Punic Wars: A Map of Conflict and Consequence. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Punic Wars: A Map of Conflict and Consequence

The Punic Wars, a series of three brutal conflicts spanning over a century (264-146 BCE), stand as a testament to the clash of titans in the ancient world. Rome, the burgeoning power of the Italian peninsula, found itself locked in a struggle for dominance with Carthage, a wealthy and formidable maritime empire centered in North Africa. These wars, fought across the Mediterranean Sea, shaped the course of history, leaving an indelible mark on the political, social, and cultural landscape of the ancient world.
A Visual Representation of Conflict:
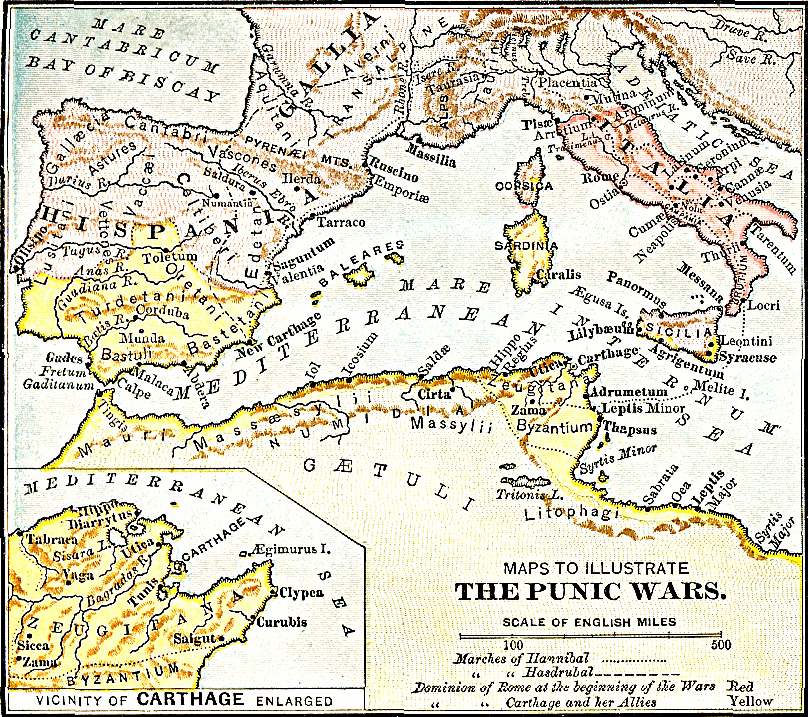
The Punic Wars map, a crucial tool for understanding the ebb and flow of these epic struggles, serves as a visual chronicle of battles, alliances, and territorial shifts. It illustrates the vast geographical scope of the conflicts, encompassing the Mediterranean basin, from the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the shores of Greece in the east.
Understanding the Importance of the Map:
The map provides a comprehensive overview of the key locations and events that defined the Punic Wars:
- The Western Mediterranean: The map highlights the strategic importance of Sicily, a vital island in the heart of the Mediterranean. Both Rome and Carthage recognized its strategic value, leading to intense battles for control. The map showcases the key battles fought on Sicilian soil, including the Battle of Agrigentum, the Battle of Himera, and the Siege of Syracuse.
- The Iberian Peninsula: Carthage’s control over the Iberian Peninsula, particularly its lucrative silver mines, fueled its economic and military power. The map depicts the Roman conquest of Iberia, culminating in the Siege of Saguntum, which marked the beginning of the Second Punic War.
- North Africa: Carthage’s home base, North Africa, was a vital source of manpower and resources. The map showcases the decisive battles fought on African soil, including the Battle of Zama, where Scipio Africanus decisively defeated Hannibal, marking a turning point in the Second Punic War.
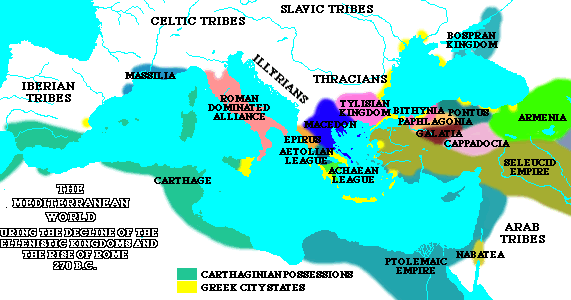
- The Eastern Mediterranean: The map also reveals the reach of the Punic Wars beyond the western basin, encompassing the eastern Mediterranean. The Roman conquest of Greece, orchestrated by the brilliant general Flamininus, is depicted on the map, showcasing the expansion of Roman power across the Mediterranean.
Key Features of the Punic Wars Map:
- Battle Locations: The map pinpoints key battle sites, allowing viewers to visualize the strategic choices made by both sides.
- Territorial Control: The map demonstrates the changing territorial control throughout the wars, highlighting the ebb and flow of power between Rome and Carthage.
- Trade Routes: The map illustrates the crucial trade routes that connected the Mediterranean world, demonstrating the economic stakes involved in the Punic Wars.
- Political Alliances: The map highlights the alliances forged by both sides, showcasing the complex network of relationships that shaped the conflicts.
Benefits of Studying the Punic Wars Map:
- Visual Understanding: The map provides a visual representation of the Punic Wars, making it easier to comprehend the scope, scale, and key events of the conflicts.
- Strategic Insights: The map reveals the strategic considerations that guided the decisions of both sides, highlighting the importance of key locations and the impact of geographical factors.
- Historical Context: The map helps to understand the historical context of the Punic Wars, placing them within the broader framework of ancient Mediterranean history.
- Understanding the Rise of Rome: The map demonstrates the relentless expansion of Roman power, showcasing the strategic and military prowess that led to their eventual dominance.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What were the main causes of the Punic Wars?
A: The Punic Wars were primarily driven by competition for resources and control over key territories in the Western Mediterranean. The rivalry between Rome and Carthage, two rising powers, escalated into conflict as they clashed over control of Sicily, the Iberian Peninsula, and the lucrative trade routes of the Mediterranean.
Q: What were the major battles of the Punic Wars?
A: The Punic Wars witnessed numerous decisive battles, including:
- The Battle of Agrigentum (262 BCE): A Roman victory that marked the beginning of Rome’s dominance in Sicily.
- The Battle of Himera (480 BCE): A decisive victory for the Greeks over the Carthaginians, preventing Carthage from establishing a foothold in Sicily.
- The Siege of Syracuse (214-212 BCE): A protracted siege that ultimately resulted in the capture of Syracuse, a key Carthaginian stronghold in Sicily.
- The Battle of Cannae (216 BCE): A stunning Carthaginian victory under Hannibal, considered one of the most decisive battles in ancient history.
- The Battle of Zama (202 BCE): A decisive Roman victory led by Scipio Africanus, effectively ending Hannibal’s threat and marking a turning point in the Second Punic War.
Q: What were the consequences of the Punic Wars?
A: The Punic Wars had profound consequences for the ancient world:
- Rise of Roman Power: The Punic Wars marked the rise of Rome as the dominant power in the Mediterranean. The victories over Carthage solidified Roman dominance, setting the stage for the Roman Republic’s eventual expansion across Europe and the Middle East.
- Decline of Carthage: The Punic Wars devastated Carthage, leading to its eventual destruction in 146 BCE. The city was razed to the ground, its citizens enslaved, and its empire dissolved.
- Expansion of Roman Empire: The Punic Wars marked a turning point in Roman history, initiating a period of rapid expansion and conquest. The wars provided Rome with valuable military experience, strategic resources, and the confidence to pursue further conquests.
- Cultural Exchange: The Punic Wars facilitated cultural exchange between Rome and the Carthaginian world, introducing new ideas, technologies, and practices to both cultures.
Tips for Understanding the Punic Wars Map:
- Study the Key Locations: Familiarize yourself with the major battle sites, strategic locations, and key cities mentioned on the map.
- Trace the Territorial Shifts: Observe the changes in territorial control throughout the wars, noting the gains and losses of both sides.
- Analyze the Trade Routes: Understand the importance of trade routes and their impact on the strategies and alliances of both Rome and Carthage.
- Consider the Context: Place the Punic Wars within the broader context of ancient Mediterranean history, understanding the political, social, and economic factors that shaped the conflicts.
Conclusion:
The Punic Wars map serves as a powerful visual tool for understanding the epic struggle between Rome and Carthage. It showcases the vast geographical scope of the conflicts, the strategic considerations that guided both sides, and the profound impact these wars had on the ancient world. By studying the map, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and significance of these historical events, recognizing their lasting impact on the course of Western civilization.
![Map of the Punic Wars (264-201 BC) [4410X3000] : r/Tunisia](http://orig11.deviantart.net/f300/f/2013/061/d/e/rome_and_carthage___the_punic_wars__264___201_bc__by_undevicesimus-d5f2fuw.jpg)





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Punic Wars: A Map of Conflict and Consequence. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!