The Annexation of Texas: A Map of Expansion and Conflict
Related Articles: The Annexation of Texas: A Map of Expansion and Conflict
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Annexation of Texas: A Map of Expansion and Conflict. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Annexation of Texas: A Map of Expansion and Conflict
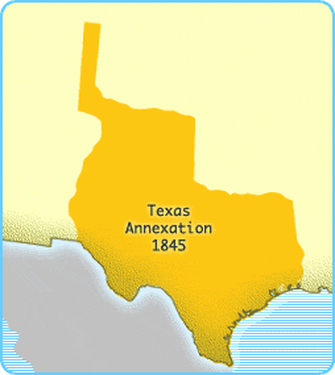
The annexation of Texas by the United States in 1845 marked a pivotal moment in American history, shaping the nation’s westward expansion and contributing to the eruption of the Mexican-American War. Understanding the annexation process, its geographic implications, and its historical context is crucial to grasping the complex forces that shaped the American landscape.
A Brief History of Texas:
Texas, initially part of the vast territory claimed by Spain, gained its independence from Mexico in 1836 following the Texas Revolution. The newly formed Republic of Texas, however, faced economic and political challenges. Its vast territory, stretching from the Sabine River to the Rio Grande, was sparsely populated and lacked infrastructure. Furthermore, the Republic’s debt burden and ongoing border disputes with Mexico created a volatile environment.
The Annexation Process:
The annexation of Texas was a contentious issue in the United States, dividing the nation along sectional lines. Proponents of annexation, primarily from the South, saw it as a way to expand slavery and bolster their political power. Opponents, primarily from the North, feared it would exacerbate the already tense debate over slavery and lead to conflict with Mexico.
In 1844, the United States presidential election was largely centered on the issue of annexation. James K. Polk, a Democrat who campaigned on a platform of expansionism, defeated Henry Clay, a Whig who opposed immediate annexation. Polk’s victory signaled a shift in national sentiment towards annexation, and the issue was swiftly addressed by Congress.
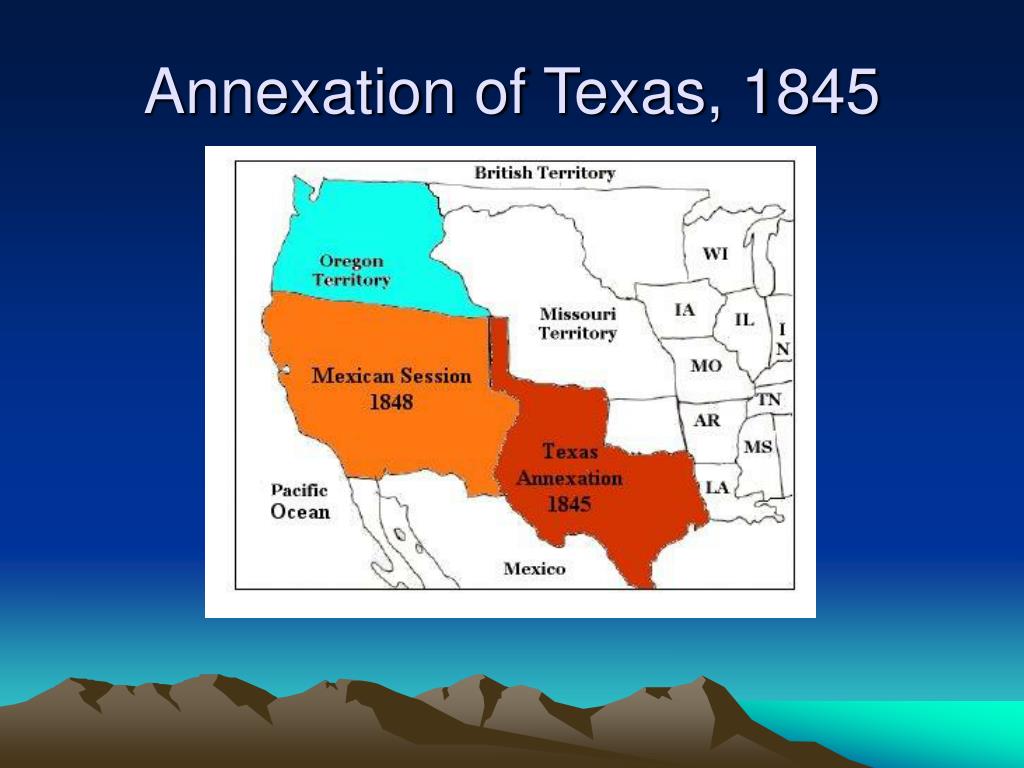
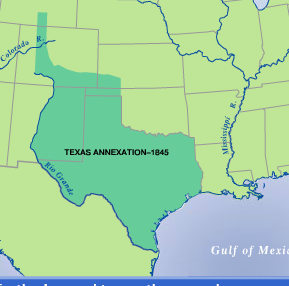
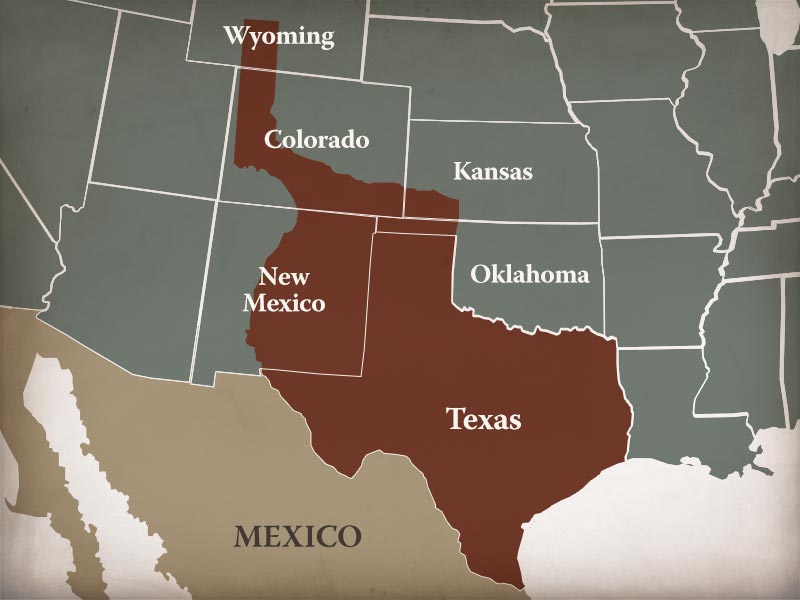
On December 29, 1845, Texas officially became the 28th state of the United States, adding over 389,000 square miles to the nation’s territory. This vast expanse encompassed the present-day states of Texas, Oklahoma, New Mexico, and parts of Colorado, Kansas, and Wyoming.
The Map and its Significance:
The annexation of Texas map is a visual representation of this significant historical event. It highlights the vast territory gained by the United States, stretching from the Louisiana Purchase in the east to the newly acquired territories in the west. The map also reveals the potential for conflict with Mexico, as the disputed border along the Rio Grande remained a source of tension.
Impact and Legacy:
The annexation of Texas had far-reaching consequences:
- Expansion of Slavery: The addition of Texas to the United States fueled the debate over slavery, as the territory was open to the institution. This contributed to the growing sectional tensions that ultimately led to the Civil War.
- Mexican-American War: The annexation of Texas triggered the Mexican-American War (1846-1848). Mexico refused to recognize Texas’ independence and viewed its annexation as an act of aggression. The war resulted in the United States acquiring vast territories, including California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, and parts of New Mexico and Colorado.
- Westward Expansion: The annexation of Texas marked a major step in the westward expansion of the United States. It opened up new opportunities for settlement, economic development, and trade. The territory also provided a strategic foothold for the United States in the Southwest, bolstering its influence in the region.
- Transformation of the American Landscape: The annexation of Texas dramatically altered the geographical and political landscape of the United States. It transformed the nation from a predominantly Atlantic-based country to one with a significant presence in the Southwest and Pacific regions.
FAQs about the Annexation of Texas:
1. What were the main reasons for the annexation of Texas?
- Economic Opportunities: The vast territory of Texas offered fertile land for agriculture, mineral resources, and potential trade routes.
- Expansion of Slavery: The annexation would allow the expansion of slavery into new territories, benefiting the Southern economy and political power.
- Strategic Advantages: Texas’ location provided the United States with a strategic foothold in the Southwest, enhancing its influence in the region.
- National Prestige: Annexing Texas would demonstrate the United States’ growing power and influence on the world stage.
2. What were the main arguments against the annexation of Texas?
- Expansion of Slavery: Opponents feared that annexation would exacerbate the already tense debate over slavery and lead to conflict.
- Conflict with Mexico: Annexation was seen as an act of aggression against Mexico, likely leading to war.
- Constitutional Issues: Some argued that annexation violated the principle of popular sovereignty, as Texas had not been granted statehood by its own citizens.
- Political Instability: Texas was known for its political instability and the potential for future conflicts.
3. How did the annexation of Texas affect the relationship between the United States and Mexico?
The annexation of Texas strained relations between the United States and Mexico, leading to the Mexican-American War. Mexico viewed annexation as a hostile act and refused to recognize Texas’ independence. The war resulted in significant territorial losses for Mexico and further deepened the rift between the two nations.
4. What were the long-term consequences of the annexation of Texas?
The annexation of Texas had a lasting impact on the United States, shaping its geographic boundaries, political landscape, and cultural identity. It contributed to the expansion of slavery, the outbreak of the Mexican-American War, and the westward expansion of the nation. The territory acquired through annexation also played a significant role in the development of the Southwest and the rise of the American West.
Tips for Understanding the Annexation of Texas:
- Study Maps: Visualizing the geographic changes brought about by annexation is crucial. Examining maps of the United States before and after 1845 can help understand the scale of the territory acquired.
- Read Primary Sources: Reading accounts from the time period, such as letters, diaries, and speeches, can provide a more nuanced understanding of the debates surrounding annexation and the perspectives of those involved.
- Explore the Role of Slavery: The expansion of slavery was a central issue in the debate over annexation. Understanding the economic and political significance of slavery in the South is essential for grasping the motivations behind annexation.
- Analyze the Mexican-American War: The annexation of Texas directly led to the Mexican-American War. Studying the causes, consequences, and historical context of this conflict is crucial for understanding the lasting impact of annexation.
Conclusion:
The annexation of Texas was a complex and consequential event in American history. It expanded the nation’s territory, fueled the debate over slavery, and triggered the Mexican-American War. The map of annexation serves as a visual reminder of this transformative period, highlighting the geographical changes and the political and social ramifications of the event. By studying the history of annexation, we gain a deeper understanding of the forces that shaped the American landscape and the ongoing debates over expansion, territoriality, and national identity.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Annexation of Texas: A Map of Expansion and Conflict. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!