Navigating the Waters of Life: A Comprehensive Exploration of Galveston Bay
Related Articles: Navigating the Waters of Life: A Comprehensive Exploration of Galveston Bay
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Waters of Life: A Comprehensive Exploration of Galveston Bay. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Waters of Life: A Comprehensive Exploration of Galveston Bay
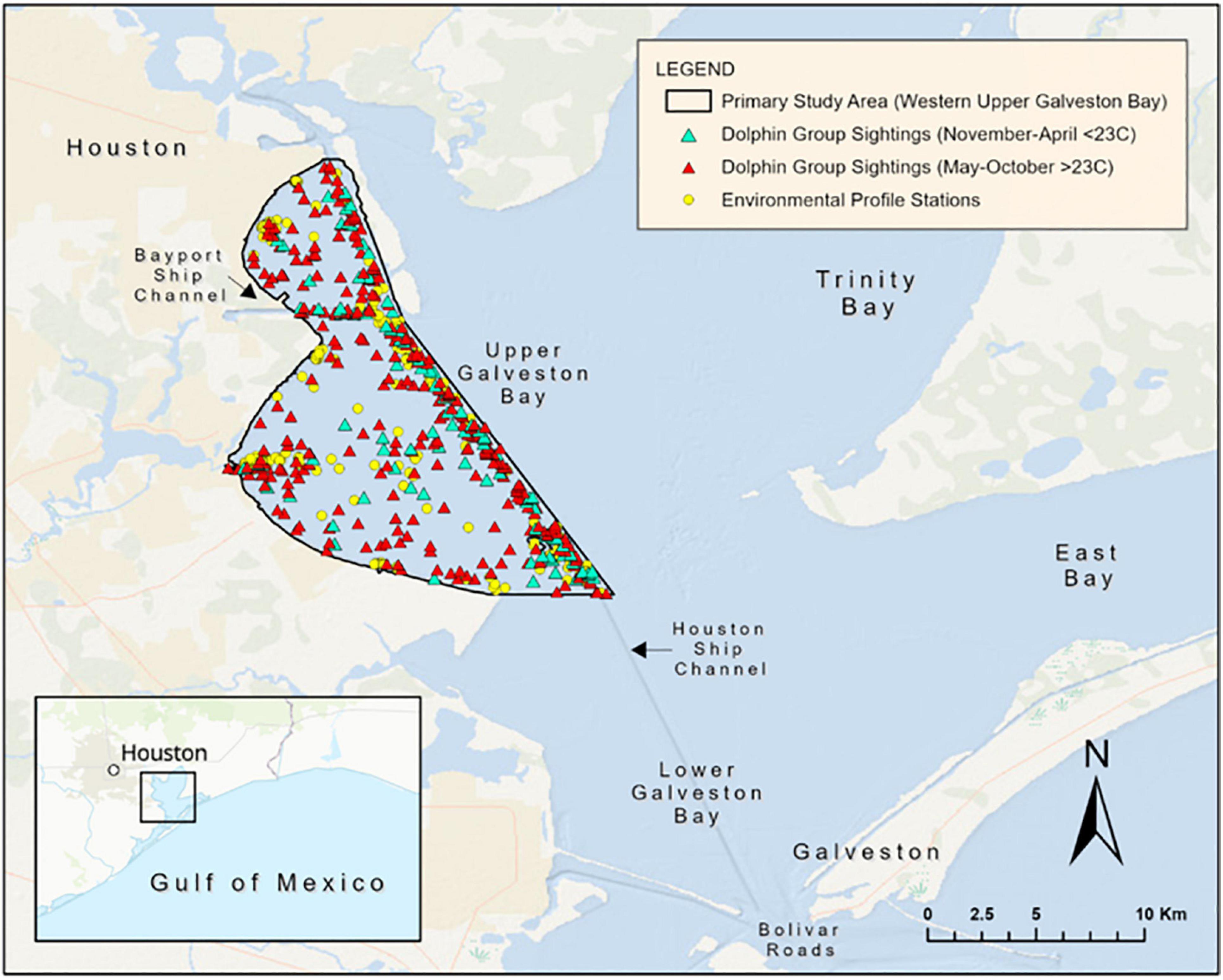
Galveston Bay, a vast expanse of water nestled along the Texas Gulf Coast, serves as a vibrant hub of ecological, economic, and cultural significance. This intricate ecosystem, a tapestry of diverse habitats, plays a crucial role in the lives of countless species and the prosperity of the surrounding communities. Understanding the intricacies of Galveston Bay, its geography, and its interconnectedness with the natural world is essential to appreciating its importance and the need for its continued preservation.
A Geographical Tapestry:
Galveston Bay, covering approximately 600 square miles, is a complex estuarine system, a unique blend of freshwater and saltwater. The bay’s geographic features contribute to its rich biodiversity and dynamic nature.
- The Mouth of the Bay: The bay’s connection to the Gulf of Mexico, through a narrow channel, allows for the constant influx of saltwater, shaping the salinity levels within the bay.
- The Trinity River: The largest freshwater source for Galveston Bay, the Trinity River flows from the north, bringing in nutrients and sediment that influence the bay’s ecosystem.
- The San Jacinto River: This river, originating in the Piney Woods of East Texas, contributes to the bay’s freshwater balance and supports diverse aquatic life.
- The Numerous Tributaries: Smaller rivers and creeks, like the Buffalo Bayou and the Clear Creek, feed into the bay, further diversifying its water sources and contributing to its ecological complexity.
- The Islands: Galveston Island, Bolivar Peninsula, and numerous smaller islands dot the bay, providing critical nesting and foraging grounds for diverse bird species and serving as important barriers against storm surges.
A Haven for Biodiversity:
Galveston Bay teems with life, showcasing an impressive array of habitats that support a diverse range of flora and fauna.
- Seagrass Meadows: These underwater prairies provide critical habitat for a vast array of fish, shrimp, crabs, and other marine life. Seagrass meadows also play a vital role in filtering water and preventing erosion.
- Salt Marshes: These transitional zones between land and water provide habitat for numerous bird species, including migratory shorebirds, as well as crabs, fish, and other invertebrates.
- Oyster Reefs: These natural structures, built by oysters, serve as important filters for the bay’s water, enhancing water quality and providing habitat for numerous species.
- Mangrove Forests: These salt-tolerant trees line the bay’s edges, providing crucial nursery grounds for fish and shrimp, as well as nesting and foraging grounds for birds.
- Tidal Flats: These mudflats, exposed during low tide, serve as feeding grounds for shorebirds and other wildlife, and play a crucial role in the bay’s nutrient cycle.
A Vital Economic Engine:
Galveston Bay is not just a haven for wildlife; it is also a vital economic engine for the region.
- Commercial Fishing: The bay supports a significant commercial fishing industry, providing livelihoods for countless individuals and contributing to the regional economy.
- Tourism: The bay’s beauty and recreational opportunities attract visitors from across the globe, boosting tourism and supporting local businesses.
- Shipping and Transportation: The bay serves as a major shipping hub, facilitating trade and commerce, and supporting the region’s industrial activities.
- Energy Production: The bay’s proximity to offshore oil and gas fields makes it a critical center for energy production, contributing to the national economy.
Facing Challenges, Embracing Solutions:
Despite its economic and ecological importance, Galveston Bay faces numerous challenges, many stemming from human activities.
- Pollution: Runoff from urban areas, industrial activities, and agricultural practices can introduce pollutants into the bay, degrading water quality and harming wildlife.
- Habitat Loss: Coastal development, dredging, and other human activities can destroy critical habitats, impacting the bay’s biodiversity.
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels, increased storm intensity, and shifts in precipitation patterns pose significant threats to the bay’s ecosystem.
Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative effort, involving government agencies, businesses, and individuals.
- Water Quality Monitoring and Improvement: Implementing robust monitoring programs and promoting sustainable practices to reduce pollution and improve water quality are essential.
- Habitat Restoration and Protection: Protecting existing habitats and restoring degraded areas are crucial for maintaining the bay’s biodiversity and ecological balance.
- Sustainable Development: Balancing economic growth with environmental protection is vital for ensuring the long-term health of the bay.
FAQs about Galveston Bay:
- What is the significance of Galveston Bay? Galveston Bay is a vital ecosystem, providing habitat for a wide array of species, supporting a thriving commercial fishing industry, and serving as a crucial economic engine for the region.
- What are the major threats to Galveston Bay? Pollution, habitat loss, and climate change pose significant threats to the bay’s ecosystem.
- How can I contribute to the protection of Galveston Bay? Reduce your environmental footprint, support organizations working to protect the bay, and advocate for sustainable practices.
- What are the key features of Galveston Bay’s geography? The bay is a complex estuarine system, influenced by the Gulf of Mexico, the Trinity River, and numerous other tributaries.
- What are some of the unique habitats found in Galveston Bay? Seagrass meadows, salt marshes, oyster reefs, mangrove forests, and tidal flats are just some of the diverse habitats found within the bay.
Tips for Engaging with Galveston Bay:
- Explore the Bay: Take a boat tour, kayak, or paddleboard through the bay to experience its beauty firsthand.
- Visit the Galveston Island State Park: This park offers scenic views of the bay and opportunities for birdwatching, hiking, and fishing.
- Support Local Businesses: Patronize businesses that prioritize environmental sustainability and contribute to the bay’s health.
- Volunteer: Join organizations working to protect and restore Galveston Bay.
- Educate Yourself: Learn about the bay’s ecosystem, the challenges it faces, and the solutions being implemented to protect it.
Conclusion:
Galveston Bay, a vital ecosystem and a cornerstone of the Texas Gulf Coast, demands our attention and commitment. Understanding its unique geography, its rich biodiversity, and the challenges it faces is essential for appreciating its importance and for ensuring its continued health for generations to come. Through collaborative efforts, we can work towards a future where the waters of Galveston Bay remain a vibrant tapestry of life, a testament to the interconnectedness of nature and the power of human action.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Waters of Life: A Comprehensive Exploration of Galveston Bay. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!