Navigating Michigan’s Inland Waters: A Guide to the State’s Abundant Lakes
Related Articles: Navigating Michigan’s Inland Waters: A Guide to the State’s Abundant Lakes
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating Michigan’s Inland Waters: A Guide to the State’s Abundant Lakes. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Michigan’s Inland Waters: A Guide to the State’s Abundant Lakes

Michigan, often referred to as the "Great Lakes State," is renowned for its vast coastline along the five Great Lakes. However, the state’s aquatic treasures extend far beyond the shores of Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario. Michigan boasts over 11,000 inland lakes, a remarkable natural resource that shapes the state’s landscape, economy, and recreational opportunities. Understanding the distribution and characteristics of these inland lakes is crucial for appreciating the state’s unique geography and the diverse activities they support.
A Mosaic of Aquatic Habitats:
Michigan’s inland lakes are not uniform; they exhibit a wide range of sizes, depths, and ecological features. This diversity is largely attributed to the state’s glacial history. During the Pleistocene epoch, massive glaciers carved out the land, creating depressions that filled with meltwater, forming the countless lakes that dot the landscape today.
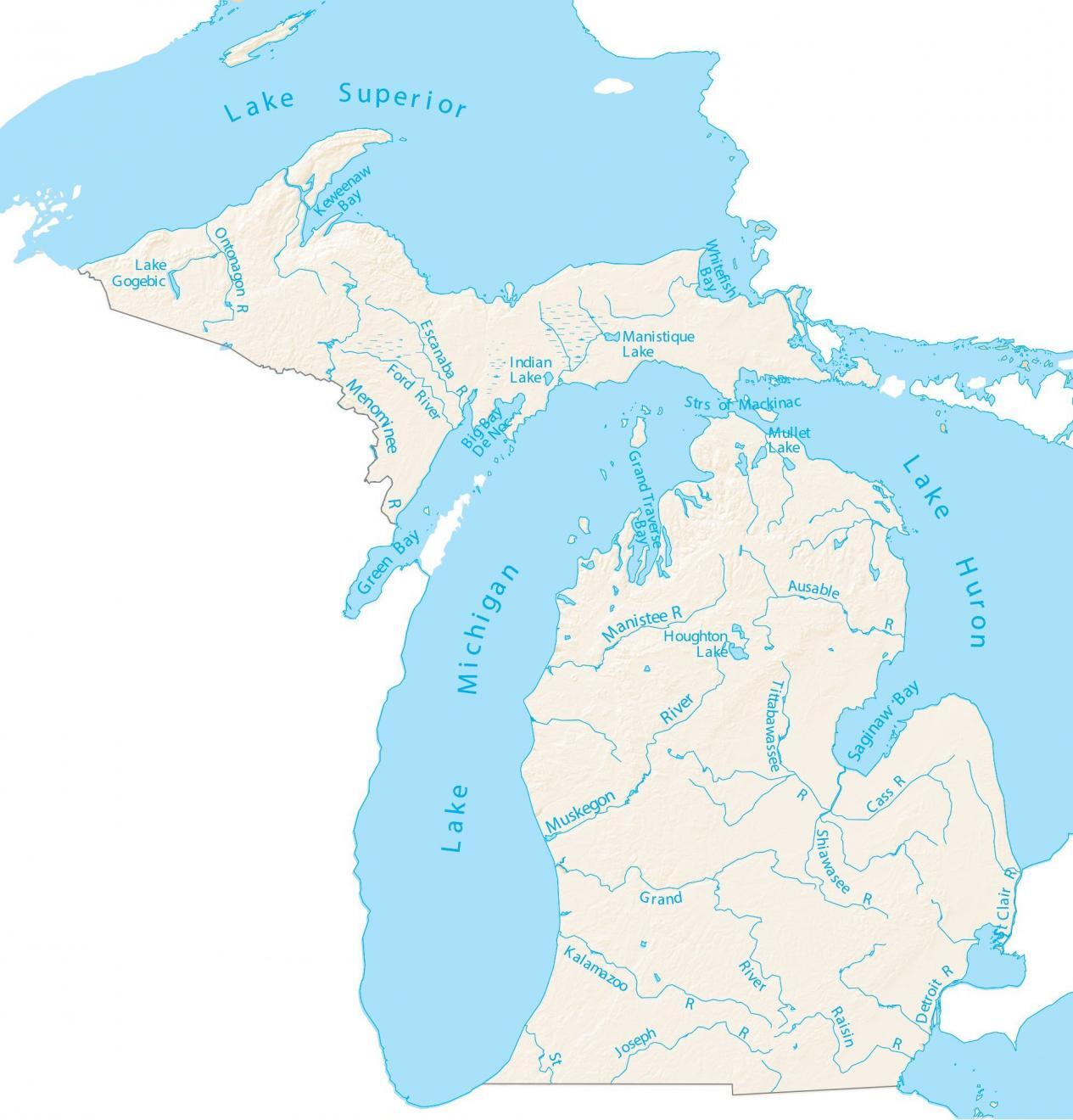
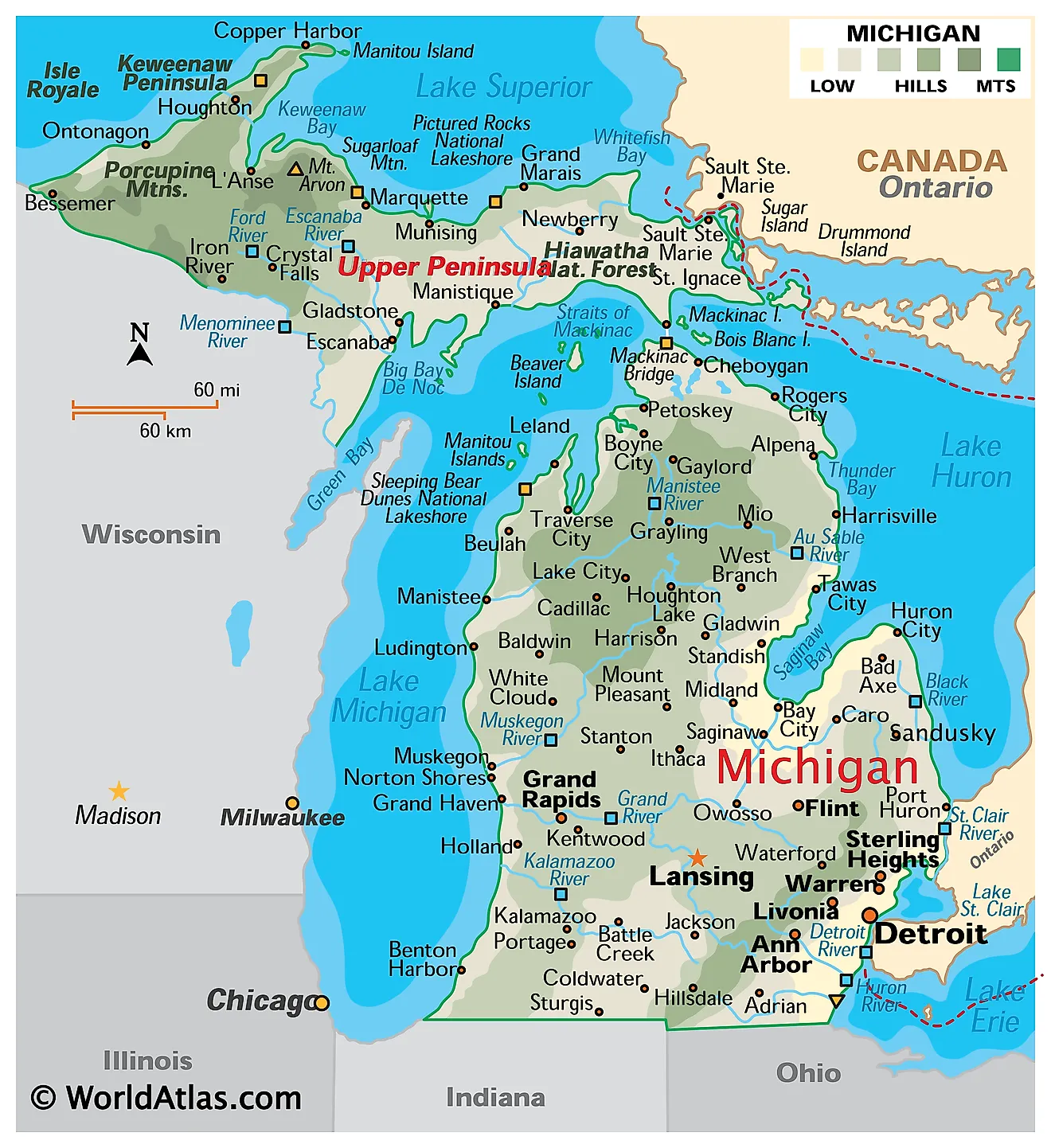
Map of Inland Lakes in Michigan: Unveiling the Landscape:
A map of Michigan’s inland lakes reveals a captivating pattern. The most concentrated clusters are found in the northern Lower Peninsula and the Upper Peninsula. These regions, heavily influenced by glacial activity, are characterized by a vast network of interconnected lakes, rivers, and streams. The southern Lower Peninsula, while possessing fewer lakes, still boasts a significant number, particularly in the central and western regions.
Navigating the Map:
Several resources provide detailed maps of Michigan’s inland lakes, including:
- Michigan Department of Natural Resources (MDNR) website: The MDNR offers interactive maps showcasing lake locations, boundaries, and key features.
- Topographical maps: These maps, available from various sources like the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), provide detailed elevation information, useful for understanding lake depths and surrounding terrain.
- Nautical charts: These maps are specifically designed for boaters, providing information on navigation channels, depths, and hazards.
Beyond Location: Understanding the Features:
A map of Michigan’s inland lakes is more than just a visual representation; it offers valuable insights into their characteristics. By examining the map, one can discern:
- Size and depth: The map’s scale and contour lines provide information about the relative size and depth of lakes.
- Connectivity: The map reveals how lakes are connected to each other through rivers and streams, forming interconnected water systems.
- Surrounding terrain: The map shows the surrounding landscape, indicating factors like elevation, land use, and proximity to urban areas.
The Importance of Michigan’s Inland Lakes:
Michigan’s inland lakes are a vital resource, contributing to the state’s economy, environment, and quality of life. Their significance is multifaceted:
- Tourism and recreation: The lakes attract millions of visitors annually, generating revenue through tourism, fishing, boating, and other recreational activities.
- Water supply: Many communities rely on inland lakes for drinking water, highlighting their importance for human consumption.
- Wildlife habitat: The lakes provide essential habitat for a diverse array of fish, birds, mammals, and other wildlife, contributing to biodiversity conservation.
- Aesthetic value: The lakes enhance the beauty of the landscape, offering scenic views and opportunities for nature appreciation.
Challenges and Conservation:
While Michigan’s inland lakes are a source of pride and economic prosperity, they face challenges:
- Water quality: Pollution from agricultural runoff, urban development, and other sources can degrade water quality, affecting aquatic life and recreational use.
- Invasive species: Introduced species can disrupt native ecosystems, causing ecological imbalances and economic losses.
- Climate change: Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and increased evaporation can impact lake levels and water quality.
Conservation efforts:
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach:
- Regulation and enforcement: Stricter regulations on pollution and invasive species are crucial to protect water quality and biodiversity.
- Public education: Educating the public about responsible lake use and the importance of conservation is essential for long-term sustainability.
- Restoration projects: Restoring degraded lake ecosystems through habitat restoration, invasive species control, and water quality improvement initiatives is critical.
FAQs about Michigan’s Inland Lakes:
Q: How many inland lakes are there in Michigan?
A: Michigan has over 11,000 inland lakes.
Q: Which region of Michigan has the most inland lakes?
A: The northern Lower Peninsula and Upper Peninsula have the highest concentration of inland lakes.
Q: What are some of the most popular inland lakes for recreation?
A: Popular lakes for recreation include Lake St. Clair, Houghton Lake, Higgins Lake, and Torch Lake.
Q: What are some of the common fish species found in Michigan’s inland lakes?
A: Common fish species include walleye, bass, pike, muskie, trout, and salmon.
Q: What are some of the threats to Michigan’s inland lakes?
A: Threats include pollution, invasive species, and climate change.
Tips for Enjoying Michigan’s Inland Lakes:
- Respect the environment: Avoid littering, dispose of waste properly, and use biodegradable products.
- Be mindful of water quality: Avoid using excessive fertilizers and pesticides near lakes.
- Learn about invasive species: Identify and report any suspected invasive species to the MDNR.
- Practice safe boating: Follow boating regulations, wear life jackets, and be aware of weather conditions.
- Support conservation efforts: Donate to organizations working to protect Michigan’s inland lakes.
Conclusion:
Michigan’s inland lakes are a remarkable natural resource, shaping the state’s landscape, economy, and quality of life. Understanding the distribution, characteristics, and importance of these lakes is crucial for appreciating their value and ensuring their long-term sustainability. By using maps, engaging in responsible lake use, and supporting conservation efforts, we can preserve this precious resource for generations to come.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Michigan’s Inland Waters: A Guide to the State’s Abundant Lakes. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!