Libya: A Nation Shaped by Geography and History
Related Articles: Libya: A Nation Shaped by Geography and History
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Libya: A Nation Shaped by Geography and History. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Libya: A Nation Shaped by Geography and History

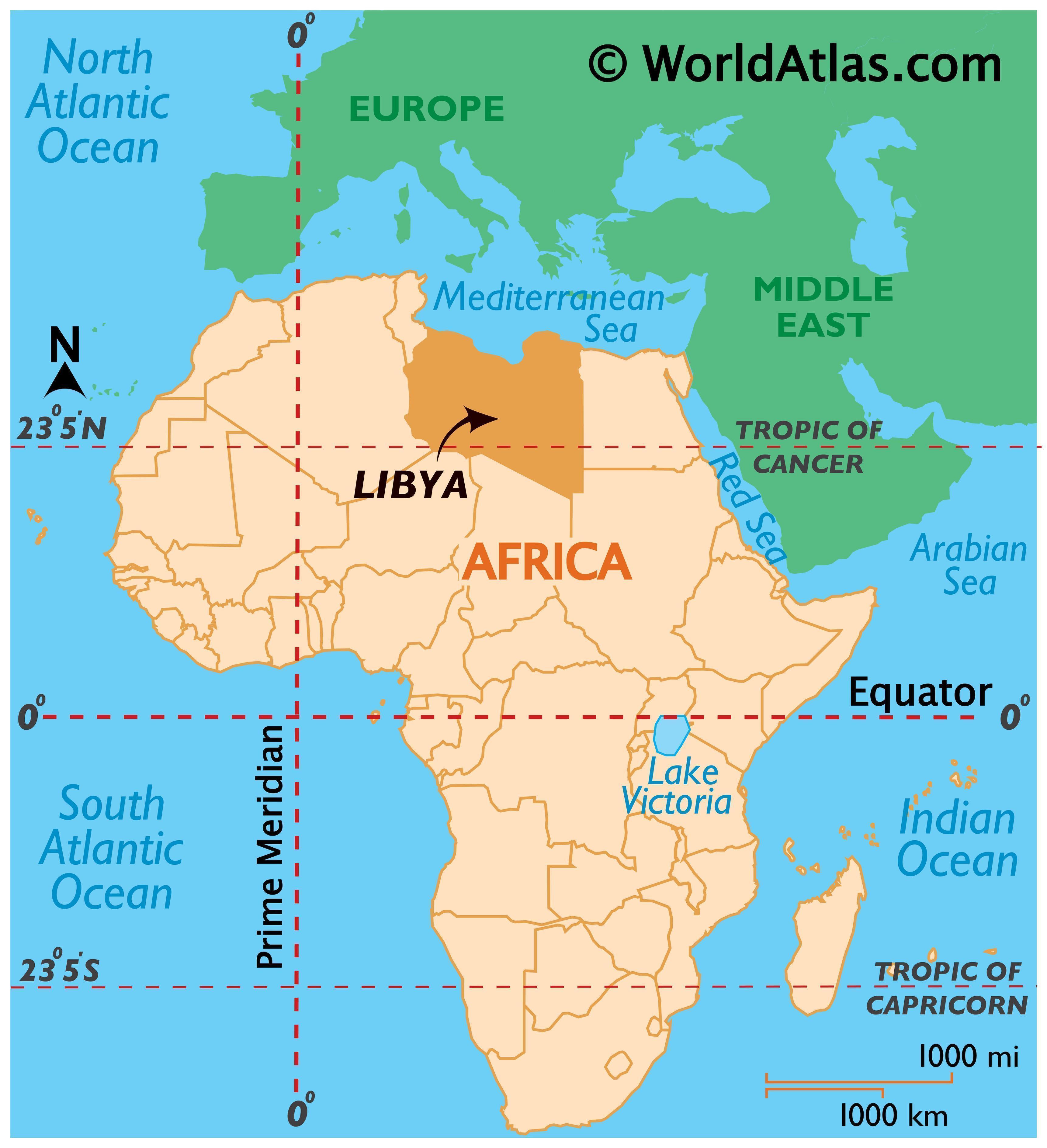
Libya, a North African nation bordering the Mediterranean Sea, occupies a vast expanse of desert landscape. Its geography, marked by vast stretches of sand dunes, rocky plateaus, and oases, has profoundly shaped the nation’s history, culture, and challenges. Understanding Libya’s geographic context is crucial for grasping its complexities and appreciating its potential.
A Land of Extremes:
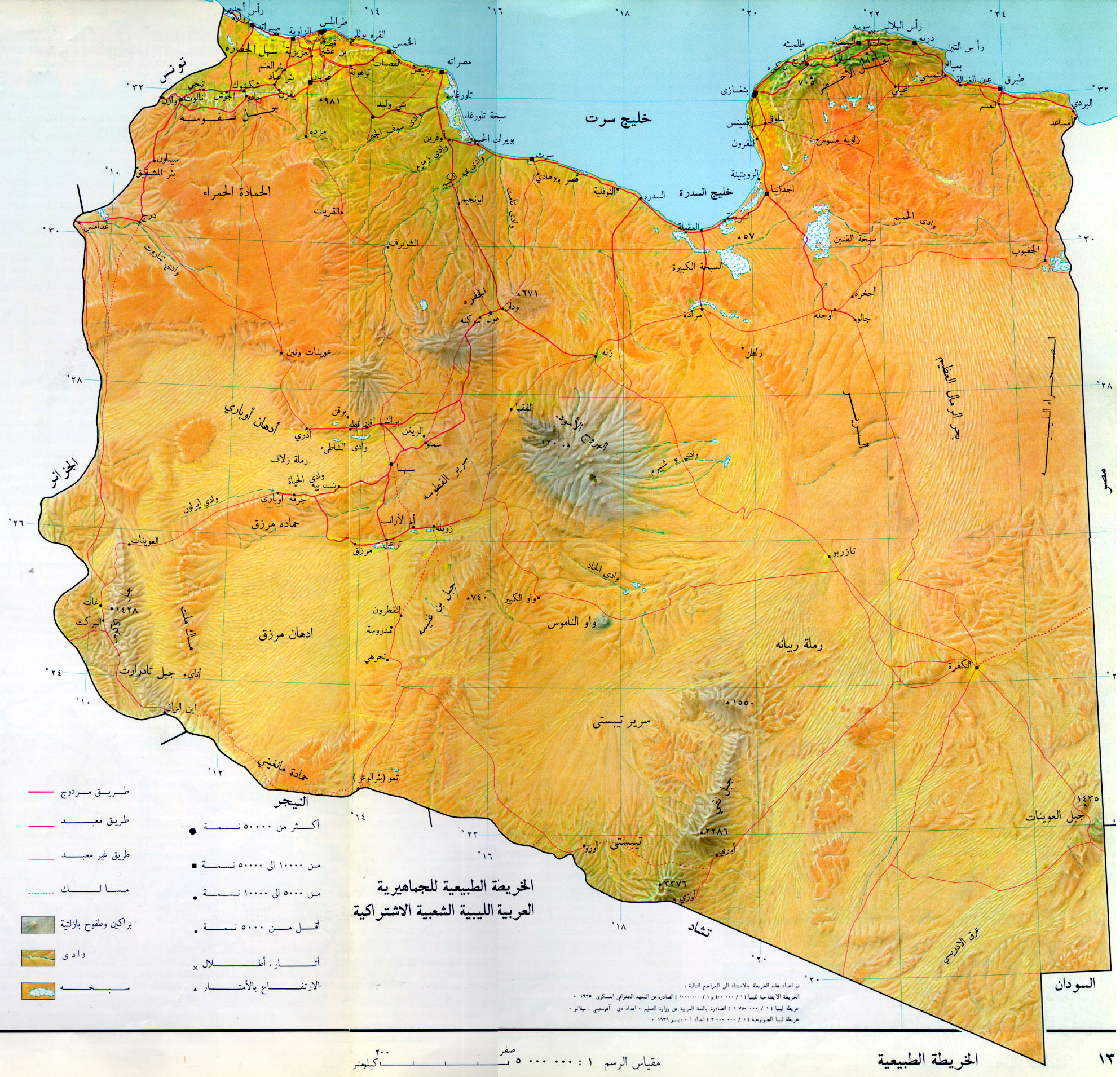
Libya’s landscape is characterized by its starkness and extremes. The Sahara Desert, the world’s largest hot desert, dominates the nation’s interior, covering approximately 99% of its territory. This vast expanse of sand and rock presents formidable challenges for human habitation, agriculture, and infrastructure development.
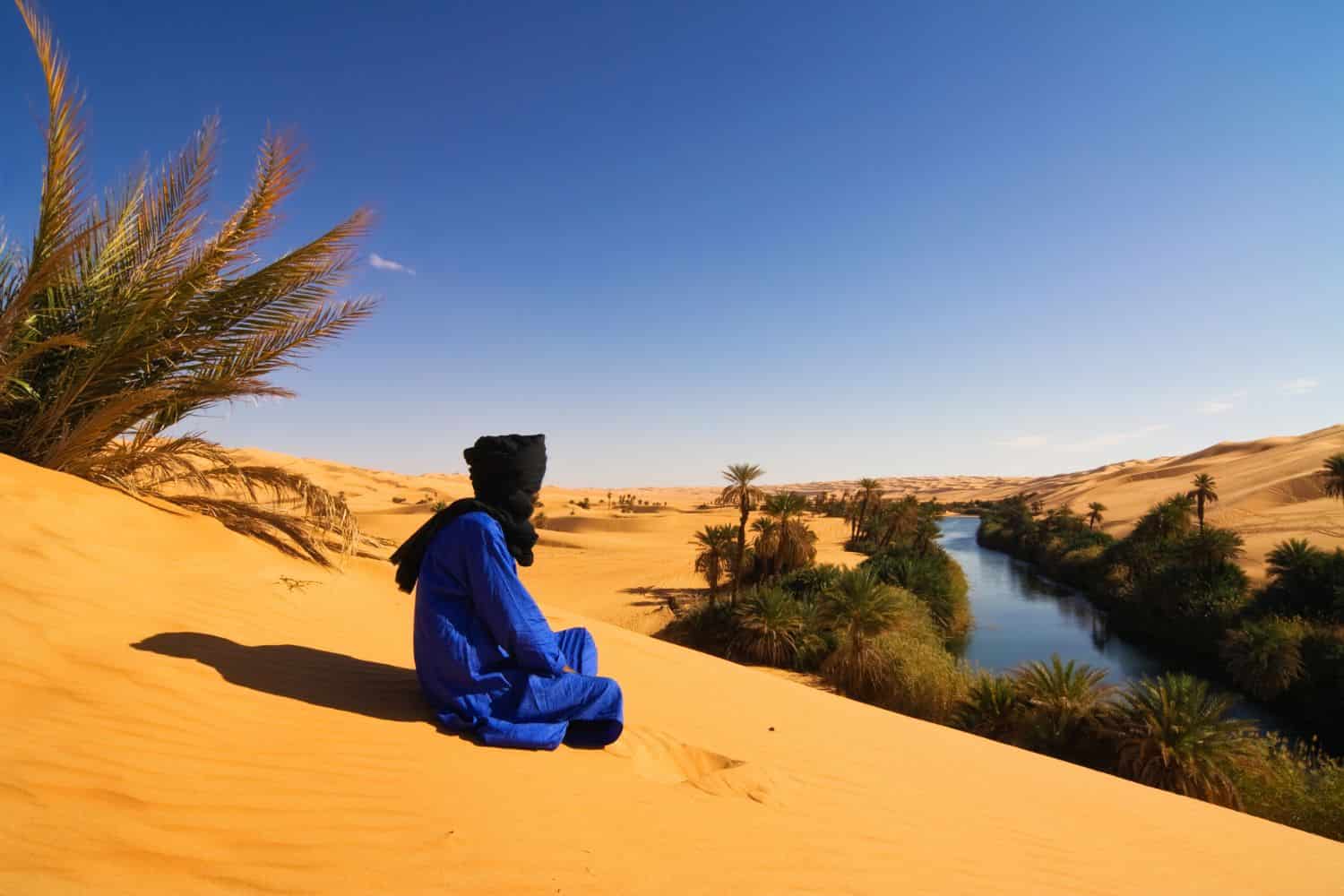
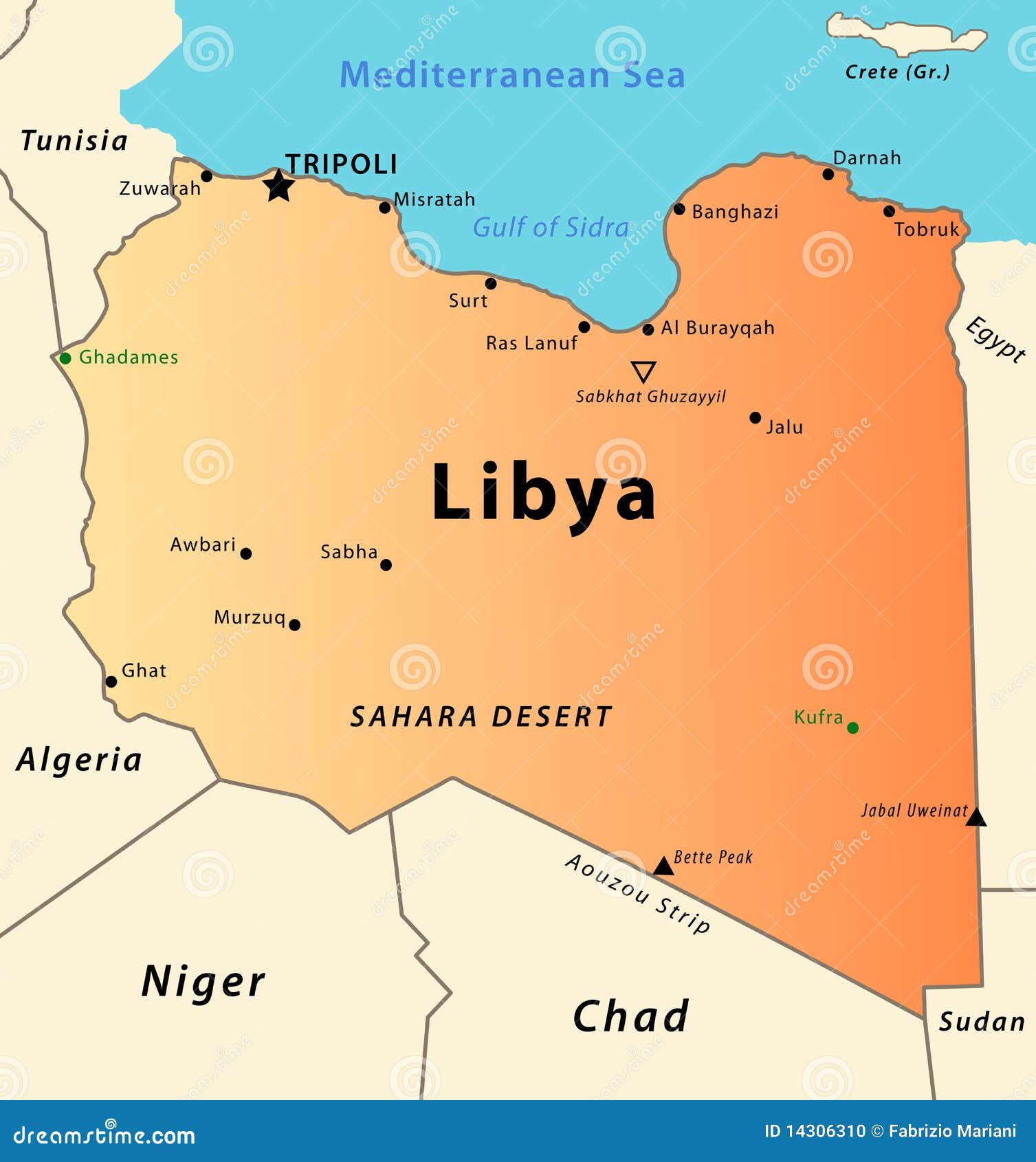
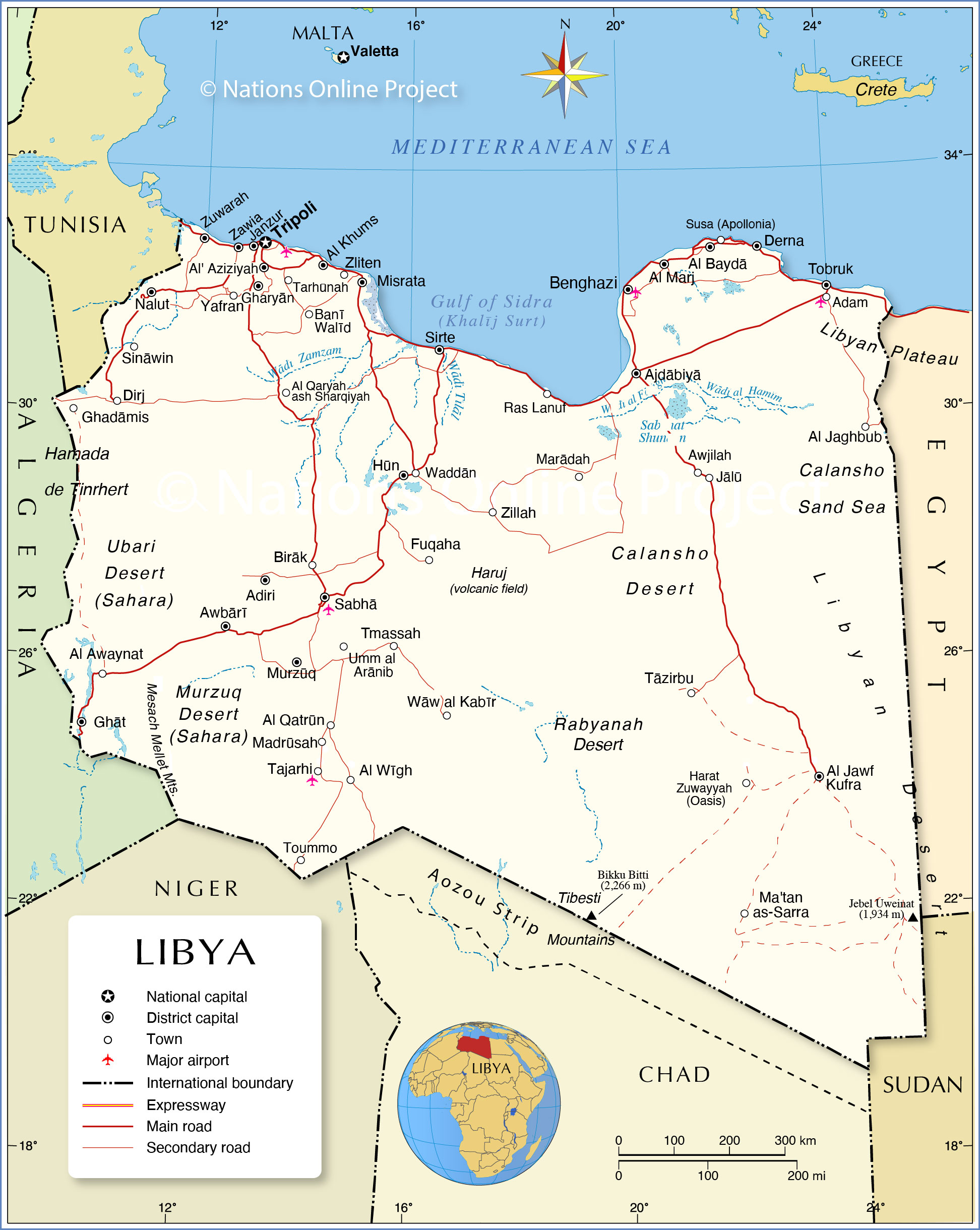
The coastal region, however, offers a stark contrast. The Mediterranean coastline, with its fertile plains and coastal oases, has historically served as a hub for trade and human settlement. Cities like Tripoli, Benghazi, and Misrata, located along the coast, have flourished as centers of commerce and culture.
Key Geographic Features:
- The Sahara Desert: The Sahara Desert, a vast expanse of arid land, dominates Libya’s landscape. Its unforgiving conditions pose significant challenges for human life and economic activities.
- The Libyan Desert: A sub-region of the Sahara, the Libyan Desert is known for its extreme dryness and lack of vegetation. It is one of the driest and hottest regions on Earth.
- The Jebel Akhdar: This mountain range in northeastern Libya provides a rare respite from the desert heat. It receives more rainfall and supports a limited amount of agriculture.
- The Fezzan Basin: Located in southwestern Libya, the Fezzan Basin is a vast depression characterized by its sand dunes, oases, and archaeological sites.
- The Mediterranean Coast: The coastline offers a unique contrast to the desert interior, providing fertile plains and coastal oases that support human life and economic activity.
Strategic Location and Historical Significance:
Libya’s strategic location at the crossroads of Africa, Europe, and the Middle East has played a pivotal role in its history. Throughout the ages, it has been a crucial route for trade and cultural exchange, attracting various empires and influences. The ancient Phoenicians, Greeks, Romans, Arabs, and Ottomans have all left their mark on Libya’s cultural tapestry.
Its location along the Mediterranean Sea has also made Libya a significant player in maritime trade and regional politics. The country’s vast oil reserves, discovered in the 1950s, further increased its strategic importance in the global energy market.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite its natural resources and strategic location, Libya faces numerous challenges:
- Water Scarcity: The arid climate and limited freshwater resources pose a significant challenge for human life and economic development.
- Political Instability: Decades of political turmoil and conflict have hindered economic progress and social development.
- Infrastructure Deficiencies: Limited infrastructure, especially in the interior, hampers economic growth and hinders access to essential services.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and desertification threaten agricultural production and water security.
However, Libya also possesses significant opportunities:
- Oil and Gas Resources: Libya’s vast oil and gas reserves offer potential for economic diversification and growth.
- Renewable Energy Potential: The abundant sunshine and wind resources present opportunities for developing renewable energy sources.
- Tourism Potential: Its unique cultural heritage, diverse landscapes, and pristine beaches offer potential for developing a thriving tourism industry.
- Strategic Location: Libya’s position at the crossroads of Africa, Europe, and the Middle East provides opportunities for regional trade and cooperation.
Understanding Libya’s Geography is Key:
To navigate the complexities of Libya’s present and future, a clear understanding of its geography is essential. Its vast desert landscape, strategic location, and diverse cultural heritage have shaped its history and continue to influence its development. Addressing the challenges and harnessing the opportunities requires a nuanced approach that considers the unique geographic context of this North African nation.
FAQs about Libya’s Geography
Q: What are the main geographical features of Libya?
A: Libya is dominated by the Sahara Desert, the world’s largest hot desert. Other key features include the Libyan Desert, the Jebel Akhdar mountain range, the Fezzan Basin, and the Mediterranean coastline.
Q: What are the challenges of Libya’s geography?
A: Libya faces challenges related to water scarcity, limited arable land, extreme temperatures, and infrastructure development in the vast desert interior.
Q: What are the benefits of Libya’s geography?
A: Libya’s strategic location at the crossroads of Africa, Europe, and the Middle East offers potential for trade and regional cooperation. Its coastline provides opportunities for maritime trade and tourism.
Q: What are the environmental concerns related to Libya’s geography?
A: Climate change, desertification, and water scarcity are major environmental concerns, posing risks to agriculture, water security, and biodiversity.
Q: How does geography influence Libya’s culture and society?
A: Libya’s geography has shaped its traditional nomadic lifestyle, its dependence on oases and underground water sources, and its cultural practices adapted to the harsh desert environment.
Tips for Understanding Libya’s Geography
- Study maps and satellite images: Visualizing Libya’s landscape can provide a better understanding of its vastness and its diverse geographical features.
- Read books and articles about Libyan geography: Researching the country’s geological history, climate, and environmental challenges can provide a deeper understanding of its geographic context.
- Explore online resources: Websites and databases dedicated to geographic information can offer valuable insights into Libya’s landscape, resources, and environmental issues.
- Connect with experts: Engaging with researchers, academics, and geographers specializing in Libya can provide valuable insights and perspectives.
Conclusion
Libya’s geography is a defining factor in its history, culture, and future. The vast expanse of the Sahara Desert, the strategic location at the crossroads of continents, and the unique challenges and opportunities presented by its landscape shape the nation’s development and its place in the world. By understanding the intricacies of Libya’s geography, we gain a deeper appreciation for its complexities and potential, paving the way for a more informed and nuanced understanding of this North African nation.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Libya: A Nation Shaped by Geography and History. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!