India: A Geographic Hub in a Diverse Neighborhood
Related Articles: India: A Geographic Hub in a Diverse Neighborhood
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to India: A Geographic Hub in a Diverse Neighborhood. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
India: A Geographic Hub in a Diverse Neighborhood
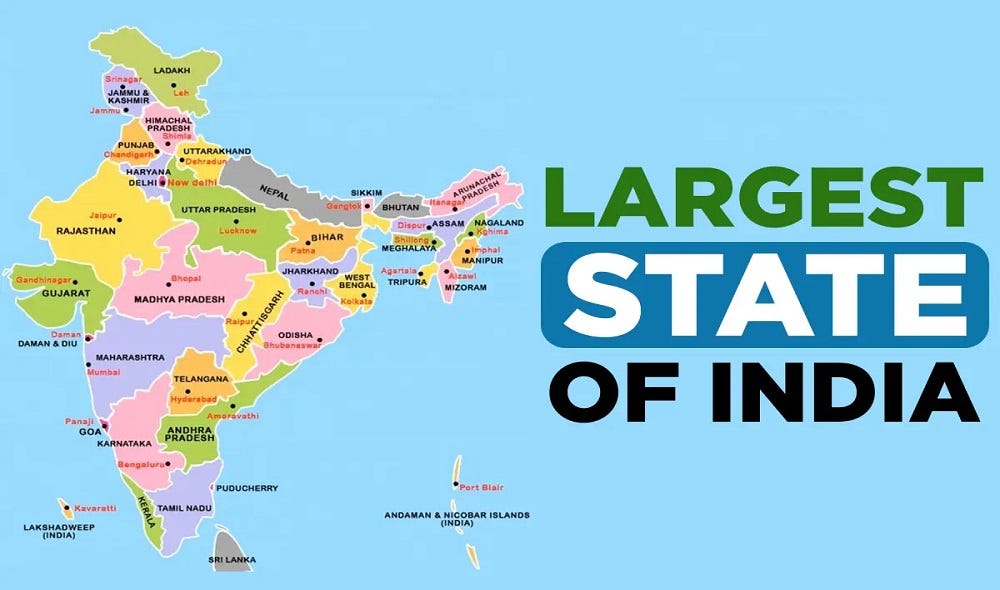
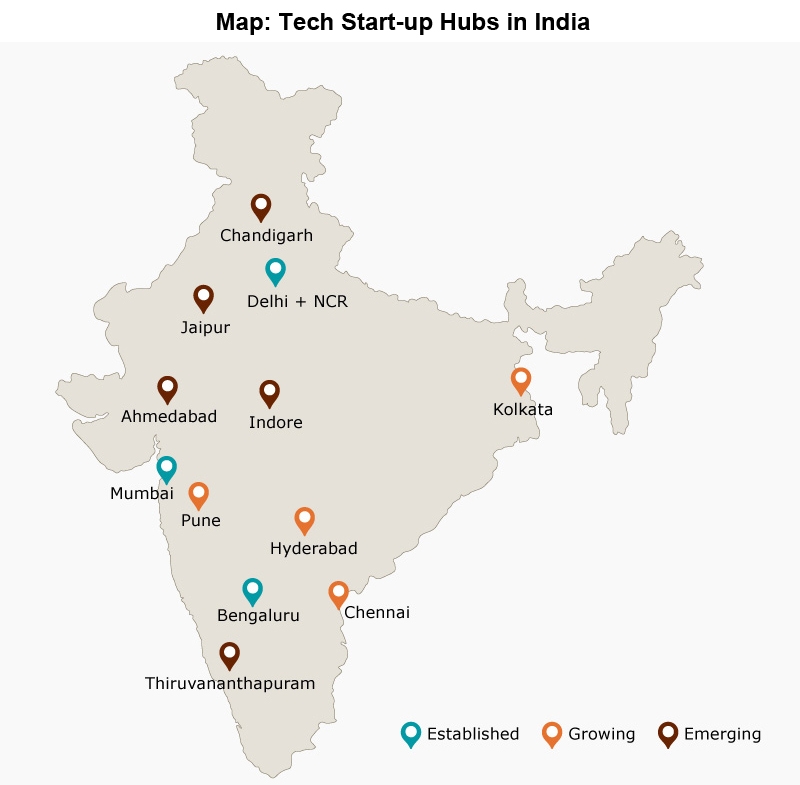
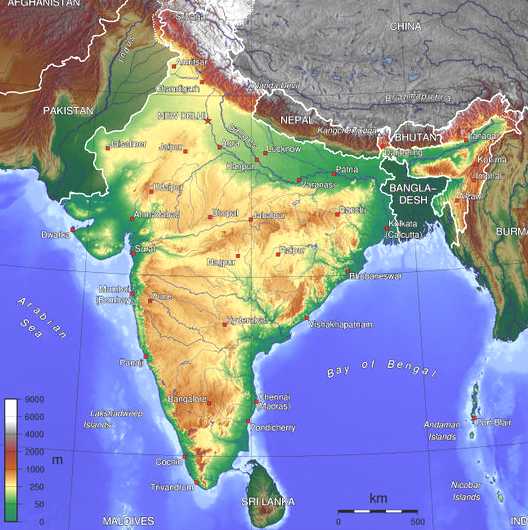
India, the world’s seventh-largest country by land area, occupies a strategically important position in South Asia. Its geographical location and unique cultural and historical tapestry have shaped its identity and influence on the global stage. Understanding the map of India and its surrounding countries is crucial for grasping the complexities of this region, its geopolitical dynamics, and its economic and cultural exchanges.
A Geographical Overview
The Indian subcontinent, home to India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives, is characterized by its diverse topography, ranging from the snow-capped Himalayas in the north to the tropical rainforests of the south. India itself encompasses a vast array of landscapes, including fertile plains, rugged mountains, coastal regions, and arid deserts.
India’s Borders:
- North: India shares its northern border with Pakistan, China, Nepal, and Bhutan. The Himalayas, the world’s highest mountain range, form a natural barrier along this border.
- East: India shares its eastern border with Bangladesh and Myanmar. The Brahmaputra River, a major waterway, flows through this region.
- West: India shares its western border with Pakistan. The Thar Desert, a vast expanse of arid land, marks this boundary.
- South: India’s southernmost point is located in the Indian Ocean, bordering Sri Lanka and the Maldives.
Surrounding Countries:
Pakistan: Situated to the west of India, Pakistan is a country of diverse landscapes, including the Indus River Valley, the Karakoram Range, and the Thar Desert. Its history and culture are deeply intertwined with India’s, with both nations sharing a common heritage.
Bangladesh: Located to the east of India, Bangladesh is a densely populated country known for its fertile deltaic plains and the Ganges River, which plays a vital role in its economy and culture.
Nepal: Nestled in the Himalayas, Nepal is a landlocked country renowned for its majestic mountains, including Mount Everest. Its rich cultural heritage and spiritual significance attract visitors from around the world.
Bhutan: Situated in the eastern Himalayas, Bhutan is a small, mountainous country known for its unique culture, its commitment to environmental conservation, and its Gross National Happiness Index.
Sri Lanka: An island nation located off the southern tip of India, Sri Lanka is known for its stunning beaches, ancient temples, and vibrant culture. Its history is marked by a blend of Indian, European, and indigenous influences.
The Maldives: An archipelago of islands located in the Indian Ocean, the Maldives is a popular tourist destination known for its pristine beaches, crystal-clear waters, and luxurious resorts.
Economic and Cultural Interdependence:
The countries surrounding India share a complex web of economic and cultural ties. Trade, investment, and cultural exchange are crucial aspects of the region’s development. The shared history, language, and cultural practices have fostered a sense of interconnectedness between these nations.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The region faces various challenges, including poverty, inequality, environmental degradation, and political instability. However, it also presents immense opportunities for collaboration and development. The countries in South Asia have the potential to leverage their collective resources and expertise to address these challenges and create a more prosperous and equitable future.
Geopolitical Significance:
The strategic location of India and its surrounding countries makes this region a geopolitical hotbed. The region’s proximity to major shipping routes, its vast natural resources, and its diverse cultural and ethnic groups make it a focal point for global powers.
FAQs on India and its Surrounding Countries:
1. What are the major rivers that flow through India and its surrounding countries?
The major rivers include the Ganges, Brahmaputra, Indus, and Yamuna. These rivers play a vital role in agriculture, transportation, and cultural life in the region.
2. What are the major mountain ranges in the region?
The major mountain ranges include the Himalayas, the Karakoram Range, and the Hindu Kush. These mountain ranges are home to some of the world’s highest peaks and have a significant impact on the region’s climate and ecology.
3. What are the major religions practiced in the region?
The region is home to a diverse range of religions, including Hinduism, Islam, Buddhism, Sikhism, Christianity, and Jainism. The presence of these different religions has shaped the region’s cultural landscape and contributed to its rich and vibrant traditions.
4. What are the major economic activities in the region?
The major economic activities include agriculture, manufacturing, tourism, and services. The region is home to a vast workforce and has the potential to become a major economic power in the world.
5. What are the major political issues in the region?
The region faces various political issues, including territorial disputes, ethnic tensions, and political instability. These issues require careful and collaborative efforts from all stakeholders to achieve lasting peace and stability.
Tips for Understanding India and its Surrounding Countries:
- Study the geography and history of the region. Understanding the physical landscape, historical events, and cultural influences will provide a deeper understanding of the region’s complexities.
- Explore the diverse cultures and traditions of the region. Engage with the local communities, learn about their beliefs, and appreciate their unique perspectives.
- Follow the news and current events in the region. Stay informed about the political, economic, and social developments that are shaping the region’s future.
- Engage in discussions and debates about the region. Share your knowledge, learn from others, and contribute to a more informed understanding of the challenges and opportunities facing the region.
Conclusion:
India and its surrounding countries are a vibrant and dynamic region with a rich history, diverse cultures, and significant economic and geopolitical importance. Understanding the map of the region and its complex dynamics is essential for navigating the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. By fostering collaboration, promoting peace and stability, and harnessing the collective potential of the region, India and its neighbors can work towards a brighter future for all.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into India: A Geographic Hub in a Diverse Neighborhood. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!