A Visual Guide to Climate Change in the United States: Understanding the Maps
Related Articles: A Visual Guide to Climate Change in the United States: Understanding the Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Visual Guide to Climate Change in the United States: Understanding the Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Visual Guide to Climate Change in the United States: Understanding the Maps
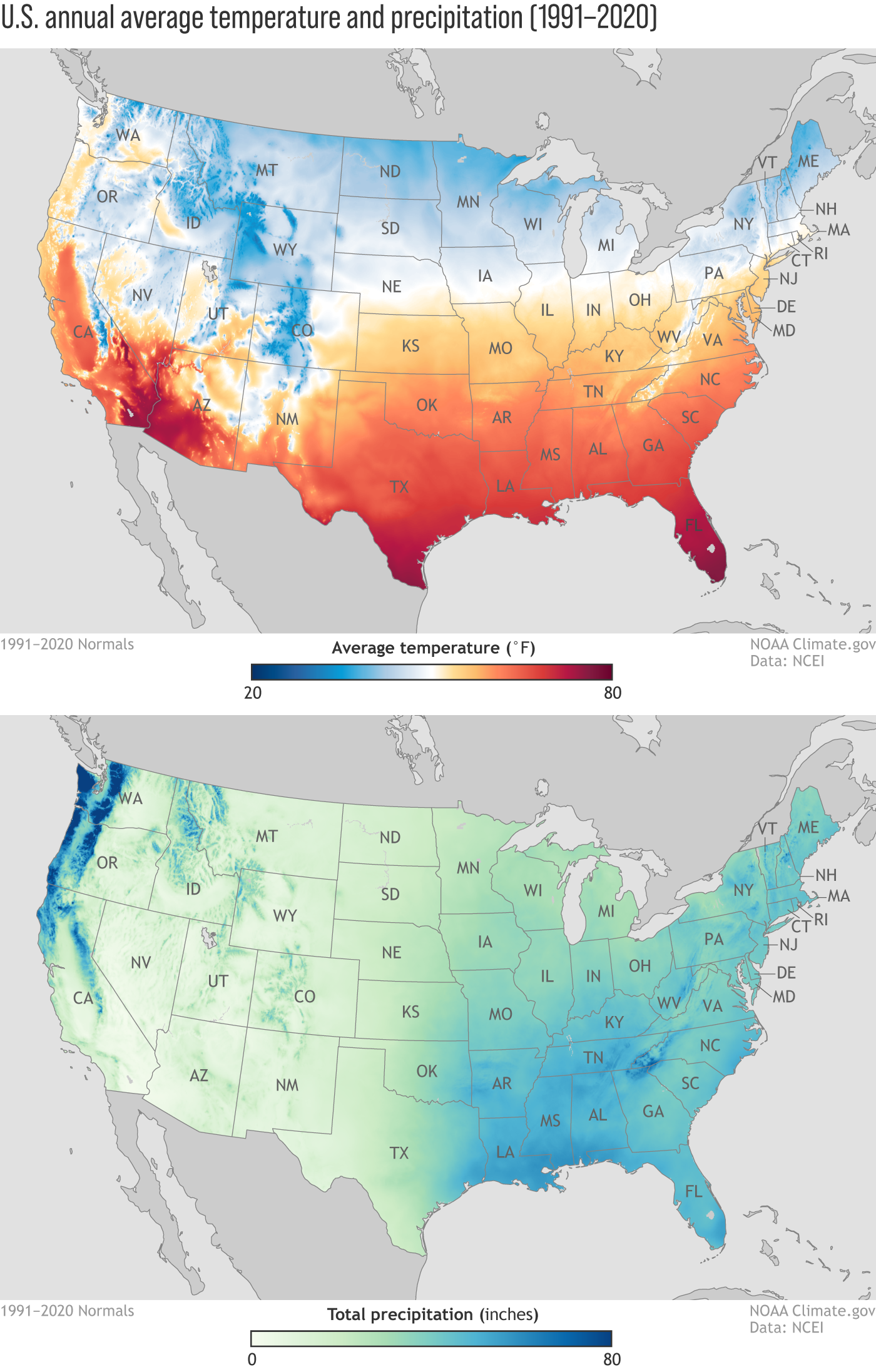
Climate change is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon, but its impacts are becoming increasingly tangible across the United States. To understand the diverse effects of climate change on different regions and ecosystems, a visual representation – a climate change map – is crucial. These maps provide a powerful tool for visualizing data, highlighting trends, and informing decision-making.
Types of Climate Change Maps:
There are various types of climate change maps that serve different purposes. Some focus on specific climate variables, while others combine multiple indicators to provide a comprehensive picture. Common types include:
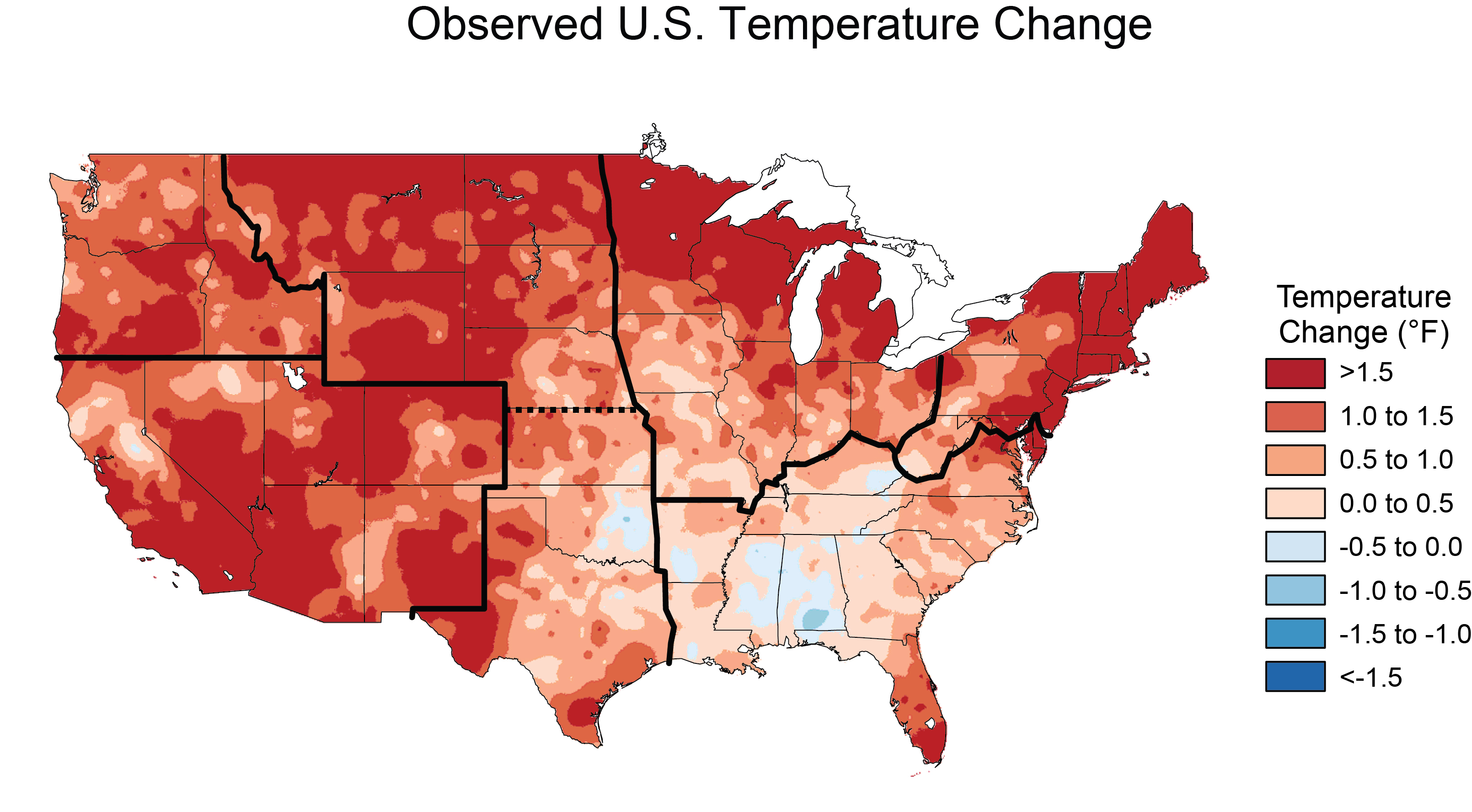
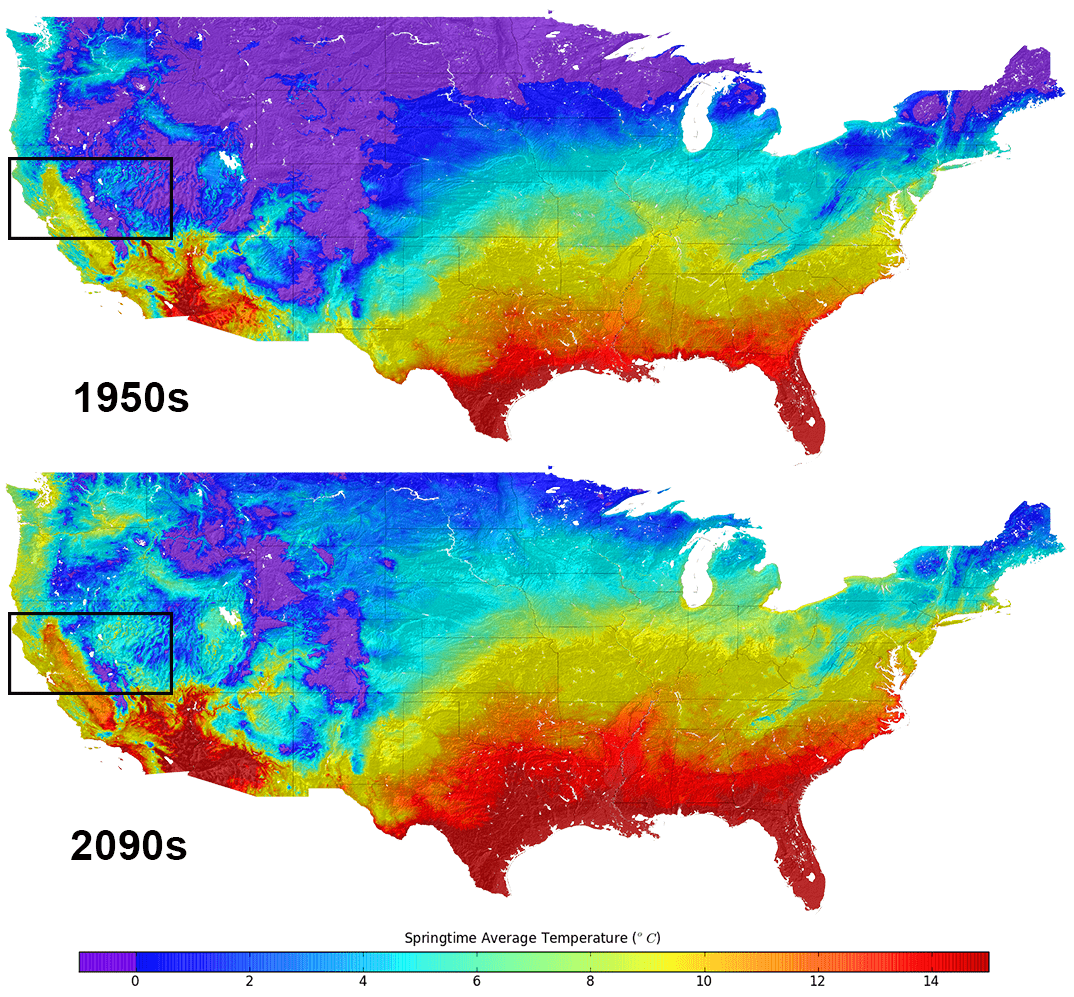
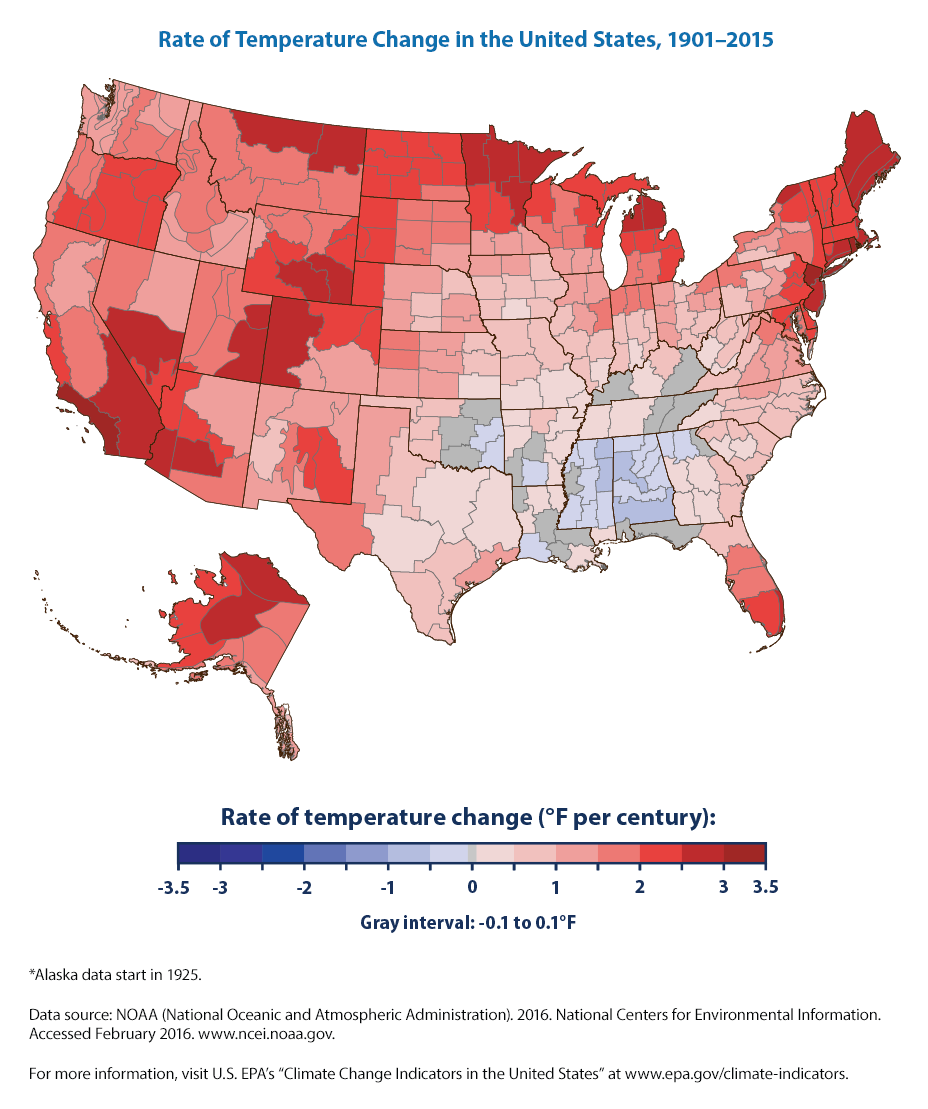
- Temperature Maps: Depicting changes in average temperatures, both historical and projected, across different regions. These maps can highlight areas experiencing accelerated warming, potentially leading to heatwaves, drought, and agricultural disruptions.
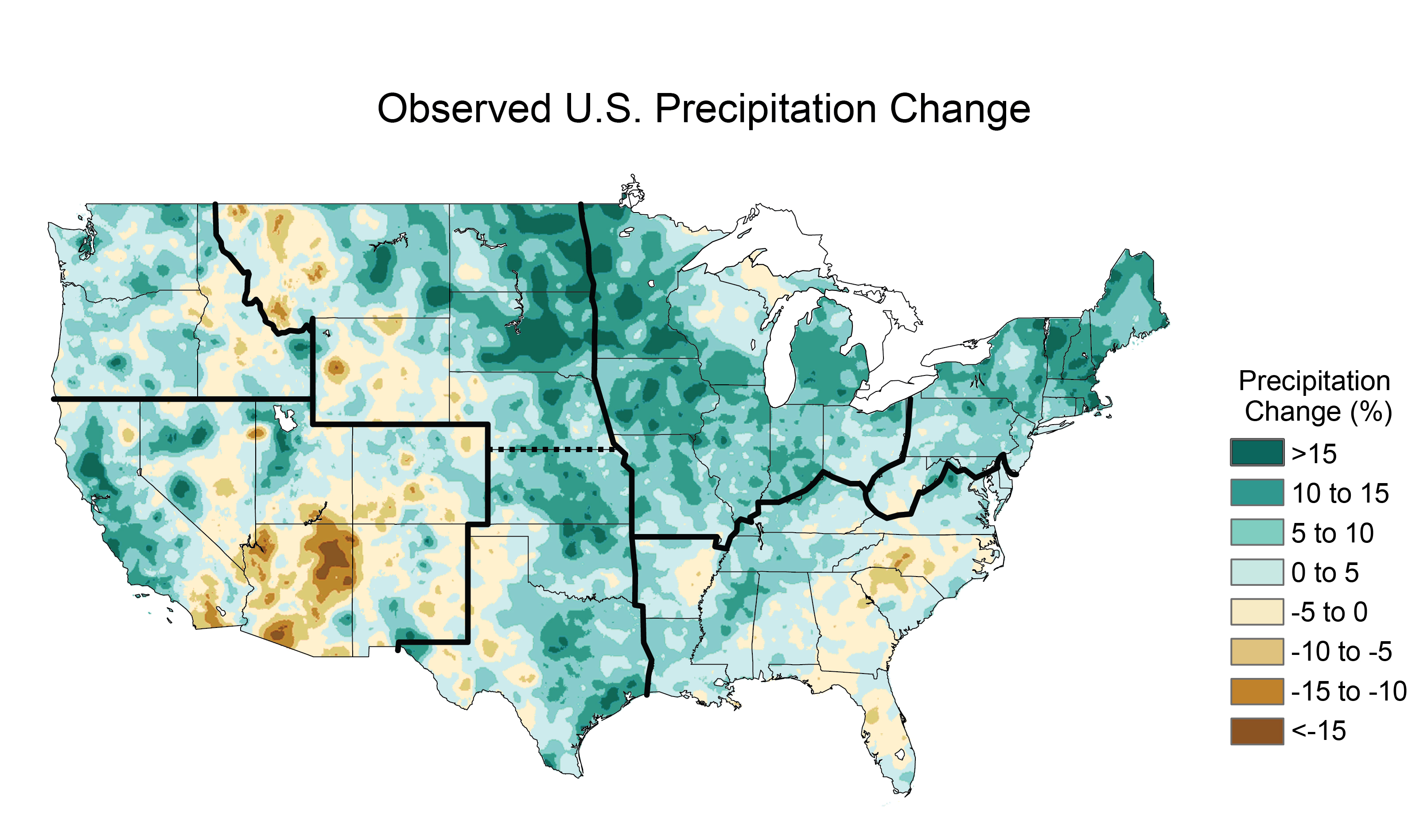
- Precipitation Maps: Illustrating changes in rainfall patterns, including increases in precipitation in some areas and decreases in others. This information is essential for understanding the potential for flooding, drought, and water scarcity.
- Sea Level Rise Maps: Showing the projected rise in sea levels, highlighting coastal areas at risk of flooding and erosion. These maps are crucial for informing coastal management strategies and planning for adaptation measures.
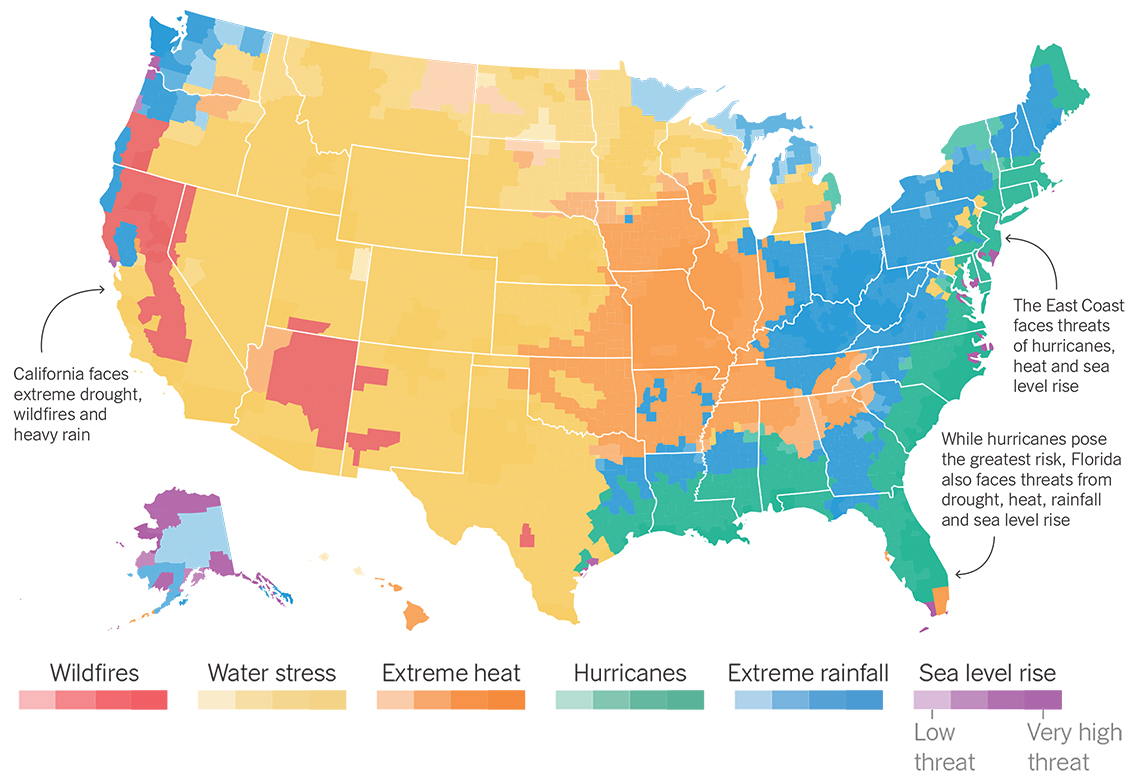
- Extreme Weather Maps: Visualizing the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events like hurricanes, tornadoes, and wildfires. These maps help identify regions most vulnerable to these events and inform disaster preparedness plans.
Benefits of Using Climate Change Maps:
- Visualizing Complex Data: Maps offer a clear and accessible way to visualize large datasets, making complex climate change information readily comprehensible.
- Identifying Trends and Patterns: By analyzing spatial patterns and trends, maps can reveal areas experiencing significant changes and pinpoint regions most vulnerable to climate impacts.
- Informing Policy and Decision-Making: Maps provide valuable data for policymakers, researchers, and communities to develop informed strategies for mitigating and adapting to climate change.
- Raising Public Awareness: Maps can effectively communicate the urgency of climate change and engage the public in understanding the impacts and potential solutions.
Key Features of Climate Change Maps:
- Data Sources: Maps rely on data from various sources, including satellite imagery, weather stations, climate models, and historical records.
- Spatial Resolution: The level of detail in a map, influencing its ability to capture localized changes.
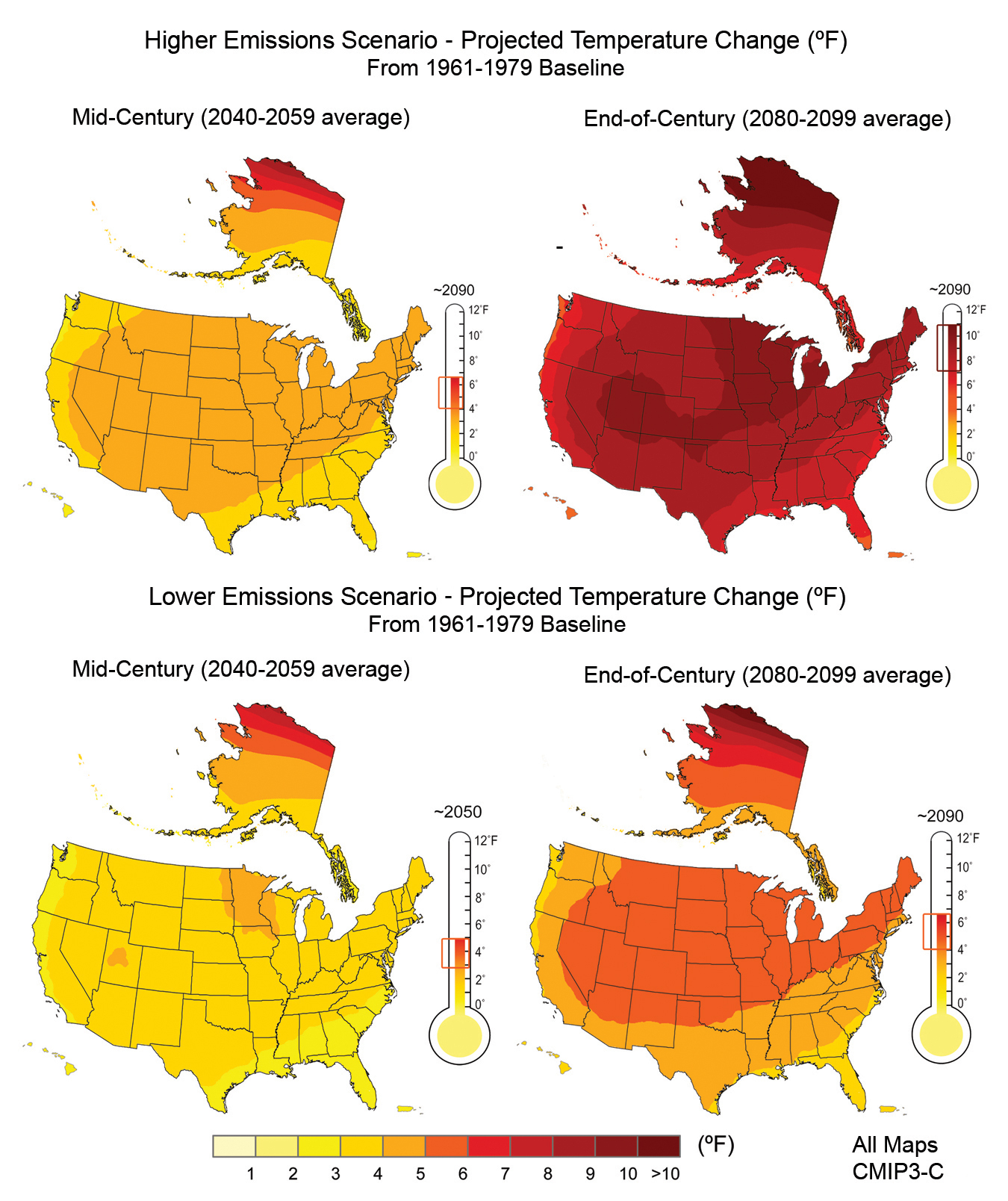
- Time Scale: Maps can depict historical data, present conditions, or project future changes.
- Projection Scenarios: Maps often present different climate change scenarios based on varying greenhouse gas emissions and other factors.
Example: The National Climate Assessment Maps:
The US Global Change Research Program publishes the National Climate Assessment, which includes numerous maps depicting climate change impacts across the country. These maps highlight key trends, such as:
- Rising Temperatures: The maps show that the average temperature across the contiguous US has increased by about 2 degrees Fahrenheit since the late 19th century.
- Increased Precipitation Extremes: The maps indicate a rise in heavy precipitation events, leading to more frequent and intense flooding.
- Sea Level Rise: The maps project that sea levels along the US coast will rise by several feet by the end of the century.
- Wildfire Risk: The maps reveal a growing risk of wildfires due to climate change, particularly in the Western US.
FAQs about Climate Change Maps:
Q: What data sources are used to create climate change maps?
A: Climate change maps utilize data from various sources, including:
- Satellite Imagery: Providing information on surface temperature, precipitation, vegetation cover, and sea level.
- Weather Stations: Measuring temperature, precipitation, wind speed, and other meteorological variables.
- Climate Models: Simulating future climate conditions based on different emissions scenarios.
- Historical Records: Providing data on past climate conditions and trends.
Q: How accurate are climate change maps?
A: The accuracy of climate change maps depends on the quality and availability of data, the sophistication of the models used, and the uncertainties inherent in climate projections. However, maps based on robust data and rigorous scientific methods provide valuable insights into current and future climate trends.
Q: What are the limitations of climate change maps?
A: Climate change maps have certain limitations, including:
- Spatial Resolution: Some maps may not capture localized changes due to coarse resolution.
- Data Availability: Data coverage and quality can vary across regions, affecting map accuracy.
- Model Uncertainties: Climate models are complex and involve inherent uncertainties, leading to variations in projections.
- Limited Representation of Impacts: Maps often focus on specific variables, neglecting other aspects of climate change impacts.
Tips for Interpreting Climate Change Maps:
- Understand the Data Sources: Familiarize yourself with the data sources used to create the map and their limitations.
- Consider the Time Scale: Pay attention to the time period covered by the map, whether historical data, present conditions, or future projections.
- Interpret the Projections: Understand the different climate change scenarios used in the map and their implications.
- Look for Patterns and Trends: Analyze the spatial patterns and trends revealed by the map to identify areas of significant change.
- Consult Multiple Sources: Compare different maps and data sources to get a comprehensive understanding of climate change impacts.
Conclusion:
Climate change maps serve as invaluable tools for visualizing and understanding the complex impacts of climate change across the United States. By providing a visual representation of data, these maps highlight areas experiencing significant changes, inform policy decisions, and raise public awareness about the urgency of addressing climate change. As climate change continues to manifest its effects, the use of climate change maps will become increasingly essential for guiding adaptation and mitigation strategies.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Visual Guide to Climate Change in the United States: Understanding the Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!