A Comparative Look at the Geography of Ohio and West Virginia: Two States, Two Distinct Landscapes
Related Articles: A Comparative Look at the Geography of Ohio and West Virginia: Two States, Two Distinct Landscapes
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comparative Look at the Geography of Ohio and West Virginia: Two States, Two Distinct Landscapes. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comparative Look at the Geography of Ohio and West Virginia: Two States, Two Distinct Landscapes
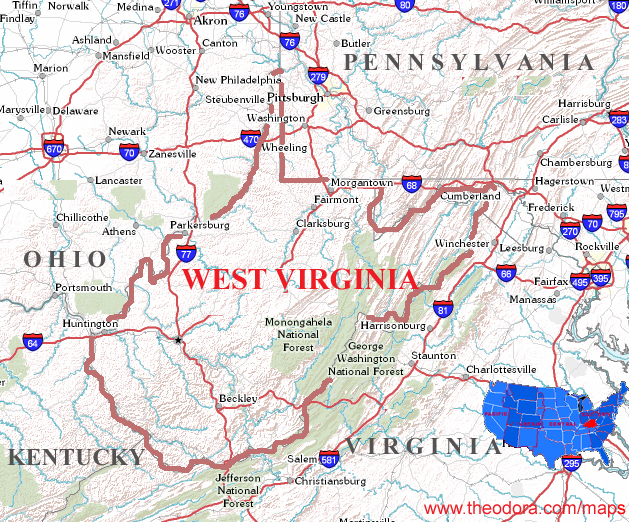
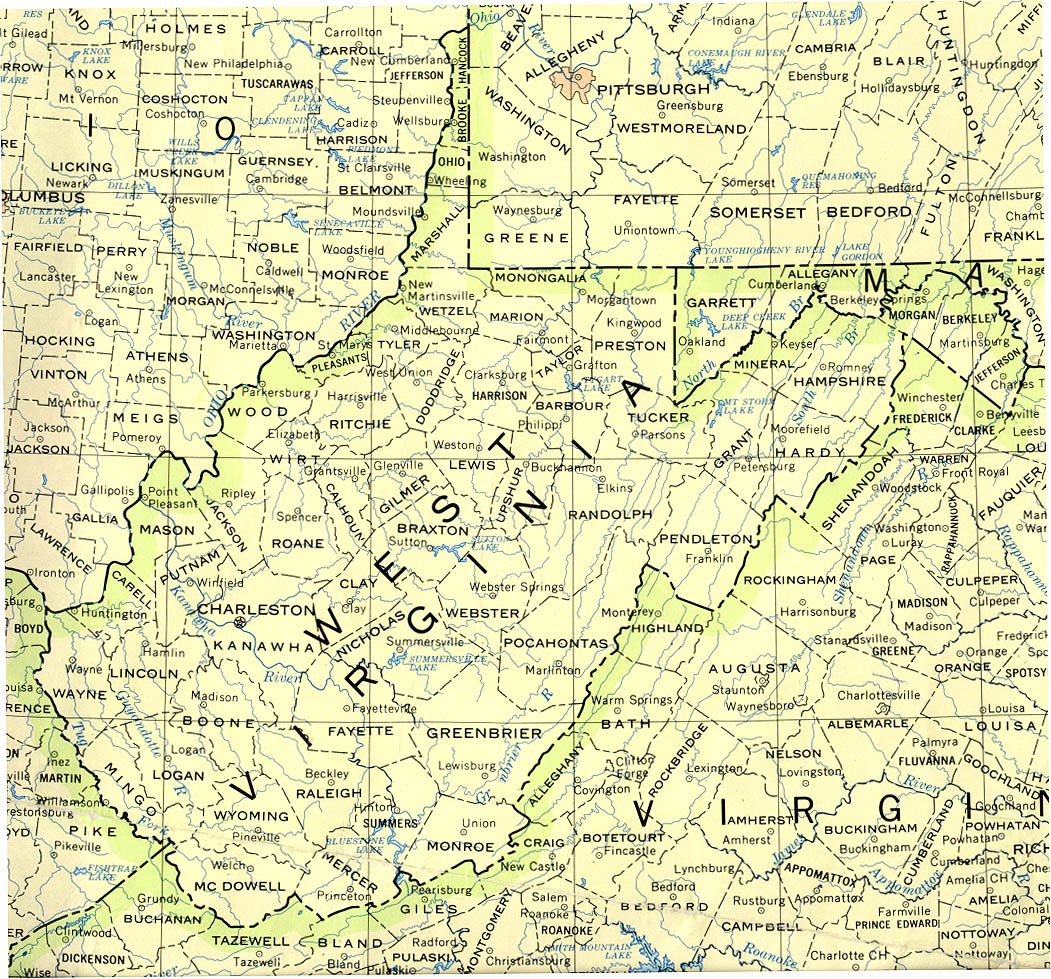
Ohio and West Virginia, neighboring states in the Appalachian region of the eastern United States, share a common history and cultural heritage. However, their landscapes, shaped by distinct geological processes, reveal stark contrasts that influence their respective economies, environments, and lifestyles.
Ohio: The Heart of the Midwest
Ohio, known as the "Buckeye State," occupies a central position in the Midwest, bordered by Lake Erie to the north and the Ohio River to the south. Its landscape is characterized by rolling hills, fertile plains, and a network of rivers and streams. The state’s geography reflects its history as a crossroads of trade and transportation, with its location facilitating the flow of goods and people across the nation.
Geological Foundations: Ohio’s landscape was shaped by the last glacial period, with the retreating glaciers leaving behind fertile soils and deposits of sand and gravel. The state’s topography is relatively flat, with the highest elevation at Campbell Hill, reaching a modest 1,550 feet. The Ohio River, a major waterway, divides the state into two distinct physiographic regions: the Allegheny Plateau in the east and the Central Lowland in the west.
A Diverse Environment: The diverse geography of Ohio supports a variety of ecosystems, from the hardwood forests of the Appalachian foothills to the wetlands and prairies of the western plains. The state is home to a rich array of flora and fauna, including white-tailed deer, black bears, and a variety of bird species.
West Virginia: The Mountain State
West Virginia, aptly nicknamed the "Mountain State," is a land of rugged beauty, defined by its towering Appalachian Mountains. The state’s landscape is characterized by steep slopes, deep valleys, and winding rivers, offering a stark contrast to the rolling hills and plains of its neighboring state, Ohio.
A Legacy of Geological Upheaval: West Virginia’s landscape is a testament to the powerful forces that shaped the Appalachian Mountains. The state is situated within the Appalachian Plateau, a region formed by the uplift of ancient sedimentary rocks. The state’s diverse geology includes coal deposits, natural gas reserves, and mineral resources, shaping its industrial development and economic history.
A Rugged and Remote Landscape: West Virginia’s mountainous terrain presents unique challenges and opportunities. Its remote locations and steep slopes have historically limited transportation and development, but also offer opportunities for outdoor recreation and resource extraction. The state’s rivers, including the Ohio River, provide vital transportation corridors and sources of hydroelectric power.
Contrasting Landscapes: A Deeper Look
The geographical differences between Ohio and West Virginia are more than just aesthetics; they have profound implications for the states’ economies, environments, and lifestyles.
Economic Diversification: Ohio’s relatively flat terrain has facilitated agricultural development and transportation infrastructure, leading to a more diversified economy. The state has a strong manufacturing base, with industries such as automotive, aerospace, and pharmaceuticals contributing significantly to its economic output. West Virginia, on the other hand, has historically relied heavily on coal mining and natural gas extraction, making its economy more vulnerable to fluctuations in energy prices.
Environmental Considerations: The contrasting landscapes of Ohio and West Virginia present unique challenges for environmental management. Ohio’s agricultural lands face the threat of soil erosion and nutrient runoff, while West Virginia’s mountainous terrain poses challenges for managing water resources and mitigating the impact of mining operations.
Cultural Influences: The geography of Ohio and West Virginia has also shaped their cultures. Ohio’s agricultural heritage and urban centers have fostered a diverse and vibrant culture, while West Virginia’s mountainous terrain has fostered a strong sense of community and a deep connection to the natural world.
FAQs about Ohio and West Virginia
Q: What are the major rivers that flow through Ohio and West Virginia?
A: The Ohio River is a shared border between the two states, while other important rivers in Ohio include the Cuyahoga River, the Scioto River, and the Maumee River. West Virginia’s major rivers include the Monongahela River, the Kanawha River, and the Cheat River.
Q: What are the highest points in Ohio and West Virginia?
A: The highest point in Ohio is Campbell Hill, at 1,550 feet. The highest point in West Virginia is Spruce Knob, at 4,863 feet.
Q: What are the major cities in Ohio and West Virginia?
A: Ohio’s major cities include Columbus, Cleveland, Cincinnati, and Dayton. West Virginia’s major cities include Charleston, Huntington, and Morgantown.
Q: What are the main industries in Ohio and West Virginia?
A: Ohio’s economy is diversified, with major industries including manufacturing, agriculture, healthcare, and education. West Virginia’s economy has historically been dominated by coal mining and natural gas extraction, but is increasingly diversifying into sectors such as tourism, healthcare, and technology.
Tips for Exploring Ohio and West Virginia
Ohio:
- Explore the Cuyahoga Valley National Park: This park offers scenic hiking trails, bike paths, and historic sites.
- Visit the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in Cleveland: This iconic museum celebrates the history of rock music.
- Experience the vibrant arts scene in Columbus: This city offers a wide range of museums, theaters, and galleries.
West Virginia:
- Hike the Appalachian Trail: This famous trail traverses the Appalachian Mountains, offering breathtaking views and challenging climbs.
- Visit the New River Gorge National River: This park offers whitewater rafting, rock climbing, and stunning scenery.
- Explore the historic towns of Harpers Ferry and Shepherdstown: These charming towns offer a glimpse into West Virginia’s rich history.
Conclusion: A Tale of Two States
Ohio and West Virginia, despite their shared history and proximity, are distinct states with unique landscapes, economies, and cultures. Their contrasting geographies have shaped their development, their environmental challenges, and their identities. Understanding the differences and similarities between these two states provides valuable insights into the complex interplay of geography, history, and human development.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comparative Look at the Geography of Ohio and West Virginia: Two States, Two Distinct Landscapes. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!